Potential Mechanism for the Prevention and Treatment Effect of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease:Aspergillus cristatus Fermented Taxilli Herba Tea Based on Process Optimization
-
摘要: 目的:建立冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶最佳工艺,探究冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶防治非酒精性脂肪肝病(non-alcoholic fatty liver disease,NAFLD)的潜在机制。方法:采用层次分析法(analytic hierarchy process,AHP),以主要化学成分和感官审评为评价指标,通过单因素实验和正交试验对冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶的加工工艺进行优化。通过“0.1%蛋黄粉+5 mmol·mL−1硫代乙酰胺”诱导斑马鱼幼鱼NAFLD模型,探究冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶对NAFLD的防治作用。通过超高效液相色谱串联-四级杆-飞行时间质谱技术(UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS)和网络药理学,筛选关键成分和核心靶点并进行分子对接。结果:最佳发酵工艺为含水量35%,渥堆时间3 h,菌液浓度1×106 CFU·mL−1,发酵时间7 d。冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶通过降低总胆固醇、甘油三酯、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇、谷草转氨酶、谷丙转氨酶达到防治NAFLD的效果(P<0.05)。通过UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS分析得到14个差异代谢物。根据14个差异代谢物的网络药理学预测结果,海胆灵、新海胆灵A等核心成分与NR1H4、LDLR、JUN、EGFR、STAT3等核心靶点对接能力良好,说明预测结果具有一定的可靠性。结论:冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶对NAFLD有明显的防治作用,且为今后的深入研究以及产品开发提供了理论基础。Abstract: Objective: Explore and establish the best process of Taxilli Herba tea fermented by Aspergillus cristatus, and dig the potential mechanism of Taxilli Herba tea fermented by A. cristatus on the prevention and treatment effect of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Methods: In order to optimize the process of Taxilli Herba tea fermented by A. cristatus, analytic hierarchy process (AHP) was applied, main chemical components and organoleptic evaluation were taken as evaluation indexes, single factor experiments were taken, and orthogonal experiment was used. Moreover, to dig and evaluate the prevention and treatment effect of NAFLD, the model in Zebrafish larval induced by 0.1% egg yolk powder and 5 mmol·mL−1 thioacetamide was used. Finally, technologies of UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS and network pharmacology were applied to select key compounds and core targets, and accomplish molecular docking. Results: The optimal fermentation process was as follows: The content of water was 35%, the time of pile-fermentation was 3 h, the concentration of A. cristatus was 1×106 CFU·mL−1, and fermentation time was 7 d. Taxilli Herba tea fermented by A. cristatus showed significant prevention and treatment effects in NAFLD (P<0.05) by lowering the level of total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL cholesterol, aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase. A total of fourteen differential metabolites was obtained by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS analysis. The network pharmacology prediction result was reliable in a certain degree, while the key compounds such as echinulin and neoechinulin A showed good docking abilities with targets including NR1H4, LDLR, JUN, EGFR, STAT3 and so on. Conclusion: Taxilli Herba tea fermented by A. cristatus had obvious preventive and therapeutic effect in NAFLD, which could provide a theoretical foundation for further research and product development.
-
非酒精性脂肪肝病(non-alcoholic fatty liver disease,NAFLD)是非过量酒精摄入影响下形成的一种肝脏脂肪蓄积过度为主要特征的代谢综合征,常伴随肝损伤、肝纤维化、肝硬化、肝细胞癌等演变式的并发症,其致病因素涵盖药物、饮食、环境、肠道菌群等方面,属多重因素相互作用的进行性疾病[1-2]。NAFLD在中国大陆的患病率接近30%[3],Estes等[4]预测中国NAFLD患病率将在2016~2030年间相对增长22.2%。目前没有特效药物被批准用于NAFLD的治疗,常采取多模式方法,以减少肝脏脂质蓄积、改善胰岛素敏感性、减少肝脏星状细胞激活等改善并发症的途径达到治疗目的[5]。降血糖的代表性药物盐酸二甲双胍常伴随厌食、腹泻等胃肠道反应,且存在乳酸中毒风险,不适用于严重肝功能不全患者,而减肥手术的快速治疗存在皮层周围炎症、肝纤维化等问题[2]。必须进一步探索除具备上述治疗目的外,还伴有抗氧化、护肝、调节肠道微生物生态等效果的治疗方式。对此,中医的多靶点治疗理念对NAFLD的防治具有明显优势[6]。
桑寄生茶是桑寄生Taxillus chinensis (DC.) Danser的叶和叶芽通过茶艺处理而成的一种别样茶(non-Camellia teas),在岭南地区,桑寄生作茶饮用历史悠久,文字记载可追溯至清代《生草药性备要》[7],“消热,滋补,追风,养血散热。作茶饮,舒筋活络。”现代研究表明,桑寄生还具有降血糖、抑制肝癌细胞、抗炎等药理作用[8]。冠突曲霉Aspergillus cristatus是茯砖茶发酵过程的主要真菌[9],可作为新型益生菌用于肥胖症的治疗[10],具有抗氧化、抗衰老、调整肠道菌群、增强宿主免疫等生物活性[11-13]。冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶是否能结合两者优势,对NAFLD的防治起到积极的影响并无报道。
斑马鱼为鲤科热带硬骨鱼,原产于南亚地区,自成为模式动物以来,因其体积小,繁殖能力强,实验周期短,基因序列与人类高度相似等特点被广泛运用于药效筛选与毒理学研究[14]。超高效液相色谱串联-四级杆-飞行时间质谱技术(UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS)是以超高效液相色谱仪作为分离系统,四级杆与飞行时间质谱为分析器串联而成的一种质谱分析技术,是近年来对于复杂基质进行鉴定分析的有效方法之一[15]。网络药理学是运用高通量组学分析,对系统生物学、基因组学、蛋白组分等多学科理论整体性分析,结合计算机模拟进行可行性分析,用于预测药物作用机制、疾病发生机制的一项技术[16]。UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS、网络药理学、斑马鱼模型等实验方法常联合使用用于中药药效预测及功能验证[17]。
基于此,本研究采用正交试验优选冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶工艺,模式动物斑马鱼探究冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶对NAFLD的防治作用,并采用超高效液相色谱串联-四级杆-飞行时间质谱技术(UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS)与网络药理学,探究冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶防治NAFLD的潜在机制。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
桑寄生茶原料 为桑寄生叶和叶芽,采摘于广西梧州岑溪市桑寄生人工种植基地,寄主植物为桑树,采摘时间2020年9月,桑寄生茶原料经广西中医药大学李永华研究员鉴定为桑寄生科植物桑寄生Taxillus chinensis (DC.) Danser的叶和叶芽;野生型(AB系)斑马鱼 购自国家斑马鱼资源中心(China Zebrafish Resource Center)。斑马鱼于本实验循环养殖系统饲养,水温20~28 ℃,环境28~30 ℃,光照/黑暗周期12 h/12 h,每天饲食丰年虾2次;总蛋白(TP)、总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、谷草转氨酶(AST)、谷丙转氨酶(ALT)测试试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;冠突曲霉(菌株编号:CICC2016.97) 中国工业微生物菌种保藏管理中心;芦丁(批号:RP210601,质量分数≥98%)、没食子酸(批号:RP191126,质量分数≥98%)、L-谷氨酸(批号:RP200602,质量分数≥98%) 成都麦德生科技有限公司;原花青素(批号:201219,质量分数≥98%) 信阳市中检计量生物有限公司;D-无水葡萄糖(批号:110833-201908,质量分数≥98%) 中国食品药品检定研究院;牛血清白蛋白(批号:NO.617C022,质量分数≥98%) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;阿托伐他汀(批号:79961,质量分数≥98%) MedChemExpress公司。
ACQUITY UPLC I-Class超高液相色谱仪 美国沃特世公司;Xevo G2-XS Tof飞行时间质谱仪 美国沃特世公司;EnVision2105高通量酶标仪筛选系 珀金埃尔默股份有限公司;UV-1780紫外可见分光光度计 岛津仪器(苏州)有限公司;Z-A-D4水生物实验养殖设备 上海海圣水族设备厂。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶工艺的正交试验优化
1.2.1.1 主要化学成分权重系数的确定
层次分析法(Analytic Hierarchy Process,AHP)[18]是根据评价指标进行成对比较的优先判断矩阵方法。根据样品主要化学成分的含量,对各个评价指标进行量化,确定为9个层级,判断矩阵评分表见表1。计算各化学成分的权重系数,并进行方法学一致性检验。
表 1 判断矩阵评分Table 1. Judgment matrix scoring table评价指标 总黄酮 茶多酚 原花
青素可溶
性糖游离
氨基酸可溶性
蛋白水浸
出物总黄酮 1 2 2 3 4 4 1/2 茶多酚 1/2 1 1 2 2 3 1/3 原花青素 1/2 1 1 1 2 2 1/4 可溶性糖 1/3 1/2 1 1 1 1 1/5 游离氨基酸 1/4 1/2 1/2 1 1 1 1/7 可溶性蛋白 1/4 1/3 1/2 1 1 1 1/8 水浸出物 2 3 4 5 7 8 1 1.2.1.2 正交试验的设计
通过前期单因素实验结果选出含水量(A)、渥堆时间(B)、菌液浓度(C)、发酵时间(D)等4因素的三水平构建L9(34)正交试验,因素水平设置如表2所示。按“常压气蒸A→渥堆B→调整含水量→常压气蒸→接种菌液C→发花D→干燥”工序进行样品制备。工序中步骤的上标字母代表该步骤考察的相关因素。
表 2 正交试验各因素水平设置Table 2. Factors of orthogonal test水平 因素 含水量(A)
(%)渥堆时间(B)
(h)菌液浓度(C)
(CFU·mL−1)发酵时间(D)
(d)1 25 1 1×105 7 2 30 2 1×106 9 3 35 3 1×107 11 1.2.1.3 主要化学成分的测定及AHP化学成分评分
对总黄酮[19]、茶多酚[20]、原花青素[21]、可溶性糖[22]、游离氨基酸[23]、可溶性蛋白[24]、水浸出物[25]进行含量测定,并以此作为考察指标进行AHP化学成分评分。
1.2.1.4 感官审评
参照GB/T 23776-2018《茶叶感官审评方法》[26]进行感官审评。感官审评得分=外形×0.2+汤色×0.15+香气×0.25+滋味×0.3+叶底×0.1。评分大致等级划分如表3所示。
表 3 各指标评分标准Table 3. Scoring criteria of each index指标 评价标准 评分 外形 形态美,色泽油润,匀整,净度好,金花茂盛,金黄,颗粒大,分布均匀 90<x≤100 形态有差异,色泽尚油润,较匀整,净度较好,金花较茂盛,黄色,颗粒较大,分布较均匀 80<x≤90 形态差异大,色泽暗,尚匀净,金花小,浅黄色,颗粒小,分布有明显差异 70<x≤80 汤色 根据发酵程度划分红浓、橙红、橙黄、黄绿等档次,明亮,澄清 90<x≤100 根据发酵程度划分红浓、橙红、橙黄、黄绿等档次,尚明亮,略有浑浊 80<x≤90 根据发酵程度划分红浓、橙红、橙黄、黄绿等档次,欠亮,浑浊 70<x≤80 香气 香气纯正,无杂气味,香高爽,香气持久 90<x≤100 香气较高尚纯正,无杂气味 80<x≤90 香气尚纯 70<x≤80 滋味 醇厚,回味甘爽 90<x≤100 尚醇厚 80<x≤90 尚醇,略有苦涩等杂味 70<x≤80 叶底 嫩度匀整,明亮,匀齐 90<x≤100 嫩度尚匀整,明亮,尚匀齐 80<x≤90 嫩度差异大,尚明,欠匀齐 70<x≤80 1.2.1.5 样品总分的计算
参考张馨宇[24]多指标综合评价方法,样品总分=100×(AHP化学成分得分/AHP化学成分得分max×0.5+感官审评得分/感官审评得分max×0.5)。
1.2.2 斑马鱼幼鱼NAFLD模型建模和桑寄生茶活性测定
1.2.2.1 样品给药浓度的确定
取健康野生型(AB系)斑马鱼以雌:雄=1:2比例于交配盒中,次日交配1.5 h后收取鱼卵,用斑马鱼胚胎水换洗5次,于恒温箱中28 ℃培养至受精后5 d(5 Day post fertilization,简称5 dpf),显微镜下挑取健康斑马鱼幼鱼用于实验研究。
分别精密称取正交试验最佳发酵样及原料样各3.000 g于250 mL锥形瓶中,加入沸水100 mL,于室温浸提45 min,过滤后用于实验。取5 dpf健康斑马鱼幼鱼于6孔板中,10条/孔,设置样品浓度为0.030、0.040、0.050、0.075、0.100、0.200、0.300、0.400、0.500、0.700 mg/mL,给药后每12 h更换一次药液,培养72 h后统计斑马鱼死亡情况,计算其72 h死亡率,确定样品给药浓度。
1.2.2.2 斑马鱼实验的构建及药效指标的确定
取5 dpf健康斑马鱼200条/缸于培养缸中培养,模型组以添加“0.1%蛋黄粉+5 mmol·mL−1硫代乙酰胺”的水溶液培养,桑寄生茶以发酵前后样品均为LC0的最大浓度给药,空白组投喂草履虫0.5 mL·500 mL−1,以120 μg·500 mL−1阿托伐他汀水溶液作阳性对照。
5 dpf斑马鱼幼鱼连续饲养72 h,空腹12 h后收样。每组随机挑取幼鱼40条于离心管中,加生理盐水100 μL,组织匀浆仪搅拌至均匀,2500 r/min离心10 min,取上清液用于TP、TC、TG、LDL-C、AST、ALT等生化指标的测定。
1.2.3 UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS色谱条件及差异代谢物筛选
1.2.3.1 溶液的制备
分别取发酵前后桑寄生茶干燥样品50 mg于50 mL 70%甲醇常温超声20 min,3000 r/min离心10 min,倒出上清液,样品加50 mL 70%甲醇重复提取一次,离心,合并上清液,定容至100 mL,过0.22 μm微孔滤膜,即得。
1.2.3.2 色谱与质谱条件
色谱柱:Thermo scientific Accucore C18柱(100×2.1 mm,2.6 μmol/L);流动相:乙腈(A)-0.1%甲酸水溶液(B),梯度洗脱:5%~95% 20 min,95% 3 min A;体积流速:0.4 mL/min;进样量:3 μL。
质谱条件:电喷雾电离源(ESI),正离子及负离子模式;一级质谱扫描范围m/z:100~1500,二级质谱扫描范围m/z:50~1500;锥孔电压:35 V;毛细管电压:2000 V;加热毛细管温度:350 ℃。
1.2.3.3 差异代谢物筛选
筛选条件:通过实验室自建数据库及公共数据库比对代谢物信息,并通过SIMCA 14.1对数据进行正交偏最小二乘判别分析(orthogonal projection to latent structure discrimination analysis,OPLS-DA)。通过OPLS-DA的VIP>1.0;结合单因素方差分析、差异倍数(Fold change,FC)≥2.0或FC≤0.5等条件筛选差异代谢物。
1.2.4 潜在机制
1.2.4.1 活性成分靶点与疾病靶点的收集
通过drugbank(https://go.drugbank.com/)、BindingDB(https://www.bindingdb.org/bind/index.jsp)、STITCH(http://stitch.embl.de/)数据库进行差异代谢物的靶点查找,个别无法查找的化合物通过SwissTraget-Prediction(http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/)预测潜在靶点。通过UniProt(http://www.uniprot.org/)规范处理差异代谢物的靶点数据。以“nonalcoholic fatty liver disease”为关键词,通过genecard(https://www.genecards.org/)查找相关疾病靶点,筛选相关性得分大于10的基因。使用Venny 2.1.0(https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/)将化合物靶点与疾病靶点进行交集处理并制作韦恩图。
1.2.4.2 PPI构建及核心靶点筛选
交集靶点上传String(https://stringdb.org),物种限定为“Homo sapiens”,获取蛋白质相互作用信息。筛选可信度(≥0.4)的网络关系,剔除游离靶点后将结果导入Cytoscape 3.6.0,根据度(degree,DE)、接近中心度(Closeness Centrality,CC)、度介中心度(Betweenness Centrality,BC)筛选核心靶点。
1.2.4.3 GO生物过程和KEGG信号通路富集分析
通过DAVID(https://david.ncifcrf.gov/tools.jsp)对共同靶点进行GO及KEGG富集分析,阈值为差异的显著性(P-value,P)<0.05,整理分析数据,选择适量数据进行Origin 2021的气泡图及Cytoscape 3.6.0的网络可视化分析。
1.2.4.4 核心靶点与关键成分的分子对接
通过Auto Dock Tools 1.5.7处理PDB数据库(https://www.rcsb.org/)下载的关键蛋白3D结构与Chem Office制作的关键成分3D结构,去水加氢后转换为pdbqt格式文件,AntoDock Vina进行分子对接,pymol进行可视化处理。根据文献[27]报道,分子对接结果的结合能<-5.0 kcal·mol−1即有较好结合活性。
1.3 数据处理
除感官审评(n=6),斑马鱼NAFLD模型试验(n=5)外,所有试验重复3次。含量及生化指标结果以平均值正负标准差(mean±SD)表示,样品评分以平均值表示。采用IBM SPSS Statistics 25.0、GraphPad Prism 9.0和Origin 2021进行数据处理,单因素方差分析统计学意义,P<0.05表示差异显著。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 正交试验结果
2.1.1 AHP构建权重系数的结果
经AHP层次研究,确定各化学成分的权重系数为总黄酮0.2121、茶多酚0.1220、原花青素0.1001、可溶性糖0.0680、游离氨基酸0.0563、可溶性蛋白0.0522、水浸出物0.3892。一致性比例因子CR=0.0081<0.10,即两两比较矩阵具有一致性,权重设置合理。AHP化学成分得分=100×[(样品总黄酮含量/总黄酮最大值)×0.2121+(样品茶多酚含量/茶多酚最大值)×0.1220+(样品原花青素含量/原花青素最大值)×0.1001+(样品可溶性糖含量/可溶性糖最大值)×0.0680+(样品游离氨基酸含量/游离氨基酸最大值)×0.0563+(样品可溶性蛋白含量/可溶性蛋白最大值)×0.0522+(样品水浸出物含量/水浸出物最大值)×0.3892]。
2.1.2 正交试验样品主要化学成分的含量测定结果
通过单因素实验和正交试验制备冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶样品,以化学成分百分含量作为评价指标,AHP评分,结果如表4所示。对9个样品的AHP评分进行方差分析,含水量、渥堆时间、菌液浓度、发酵时间等四因素的F值均大于F0.01(2,2)=99.00,即四因素对样品得分均有极显著差异(P<0.01),详见表5。
表 4 正交试验样品主要化学成分百分含量及AHP评分Table 4. Percentage content of main chemical components and AHP scores of orthogonal test samples样品 A含水量
(%)B渥堆时间
(h)C菌液浓度
(CFU·mL−1)D发酵时间
(d)总黄酮
(%)茶多酚
(%)原花青素
(%)可溶性糖
(%)游离氨基酸
(%)可溶性蛋白
(%)水浸出物
(%)AHP
评分1 1 1 1 1 1.78±0.00 2.79±0.00 0.17±0.00 2.25±0.00 0.50±0.00 0.48±0.01 19.65±0.05 90.32 2 1 2 2 2 1.68±0.00 2.98±0.00 0.17±0.00 2.20±0.01 0.41±0.00 0.50±0.01 19.99±0.07 89.62 3 1 3 3 3 1.55±0.01 2.86±0.00 0.20±0.00 2.40±0.00 0.45±0.00 0.53±0.00 18.73±0.08 87.66 4 2 1 2 3 1.56±0.01 2.78±0.00 0.17±0.00 2.20±0.02 0.42±0.00 0.47±0.01 18.33±0.05 83.96 5 2 2 3 1 1.68±0.00 2.95±0.00 0.18±0.00 2.43±0.01 0.43±0.00 0.51±0.01 20.36±0.04 91.13 6 2 3 1 2 1.72±0.00 2.87±0.00 0.24±0.00 2.54±0.04 0.45±0.00 0.74±0.01 19.46±0.06 94.10 7 3 1 3 2 1.50±0.02 2.67±0.00 0.14±0.00 2.21±0.02 0.40±0.00 0.51±0.01 18.42±0.07 81.76 8 3 2 1 3 1.52±0.00 2.72±0.00 0.13±0.00 2.25±0.00 0.40±0.00 0.48±0.01 18.86±0.04 82.77 9 3 3 2 1 1.96±0.00 2.70±0.00 0.21±0.00 2.77±0.02 0.48±0.00 0.54±0.01 19.80±0.05 95.32 表 5 方差分析Table 5. Anova analysis工艺因素 Ⅲ类平方和 自由度 均方 F值 显著性 含水量 49.903 2 24.951 1649.797 P<0.01 渥堆时间 226.240 2 113.120 7479.560 P<0.01 菌液浓度 38.852 2 19.426 1284.450 P<0.01 发酵时间 249.256 2 124.628 8240.494 P<0.01 注:F0.05(2,2)=19.00;F0.01(2,2)=99.00。 2.1.3 正交试验样品主要成分的线性回归方程
正交试验样品总黄酮、茶多酚、原花青素、可溶性糖、游离氨基酸、可溶性蛋白等主要成分的线性回归方程如表6所示。
表 6 主要考察指标线性回归方程Table 6. Linear regression equation of main indexes考察指标 线性回归方程 线性回归
决定系数R2线性范围
(mg/mL)总黄酮 y=1.25356x+0.0379851 0.9997 0.200~0.800 茶多酚 y=0.0134573x+0.0237366 0.9998 0.010~0.100 原花青素 y=5.95447x−0.0694942 0.9990 0.025~0.250 可溶性糖 y=6.04079x+0.0189998 0.9995 0.025~0.200 游离氨基酸 y=3.60380x−0.251955 0.9994 0.100~0.600 可溶性蛋白 y=4.50928x−0.0141022 1.0000 0.020~0.100 2.1.4 感官评价结果
就外形、汤色、香气、滋味、叶底等方面对正交试验样品进行感官评价,结果如表7所示。
表 7 正交试验样品感官评定结果(n=6)Table 7. Sensory evaluation results on samples of orthogonal test (n=6)样品 外形 汤色 香气 滋味 叶底 感官审评得分 评语 评分 评语 评分 评语 评分 评语 评分 评语 评分 1 形态有差异,
分布均匀84.00 橙红,明亮 90.50 香气纯正,香高爽 92.67 醇厚 90.67 嫩度匀整 84.67 89.21 2 形态有差异,
金花较茂盛85.00 橙红,明亮 90.17 香气较高尚纯正 84.50 尚醇厚 88.83 嫩度匀整,明亮,
尚匀齐89.17 87.22 3 形态有差异,
金花较茂盛85.17 橙红,明亮 90.67 香气较高尚纯正 87.67 尚醇厚 88.17 嫩度匀整 82.83 87.28 4 形态有差异 83.33 红浓,明亮 91.33 香气较高尚纯正 89.67 尚醇厚,尚甘爽 89.50 嫩度匀整,明亮,
尚匀齐89.17 88.55 5 形态有差异 83.00 橙黄,尚明亮 88.67 香气较高尚纯正 88.83 尚醇厚,尚甘爽 89.17 嫩度匀整,明亮,
尚匀齐88.17 87.68 6 形态有差异 83.67 橙黄,尚明亮 86.50 香气较高尚纯正 85.33 尚醇厚 87.83 嫩度匀整,尚匀齐 85.17 85.91 7 形态有差异,金花较茂盛,分布较均匀 85.83 橙黄,尚明亮 86.67 香气较高尚纯正 85.17 尚醇厚,略涩 83.76 嫩度匀整,明亮,
匀齐91.00 85.66 8 形态有差异,分布均匀 84.33 橙黄,尚明亮 86.83 香气较高尚纯正 88.83 尚醇厚,略涩 84.17 嫩度匀整 82.83 85.63 9 形态有差异,金花较茂盛,分布较均匀 85.33 橙黄,尚明亮 84.17 香气较高尚纯正 87.83 尚醇厚 88.17 嫩度匀整 84.17 86.52 2.1.5 多指标综合评价样品总分结果
结合主要化学成分AHP得分及感官审评得分计算正交试验样品的总分,样品总分详见表8。结合表4可知最佳工艺为A1B3C2D1或A2B3C2D1,但在实际生产中发现,含水量较低时桑寄生叶及叶芽软化、浸润程度差异较大,且“金花”较少,为确保冠突曲霉发酵效果的稳定性与均一度,选择A3B3C2D1为最佳工艺,即含水量35%、渥堆时间3 h、接种量1×106 CFU·mL−1和发酵时间7 d。
表 8 正交试验样品综合评分结果Table 8. Comprehensive evaluation on samples of orthogonal test样品 AHP化学成分得分 感官审评得分 总分 1 90.32 89.21 89.77 2 89.62 87.22 88.42 3 87.66 87.28 87.47 4 83.96 88.55 86.26 5 91.13 87.68 89.40 6 94.10 85.91 90.00 7 81.76 85.66 83.71 8 82.77 85.63 84.20 9 95.32 86.52 90.92 2.2 药效学研究结果
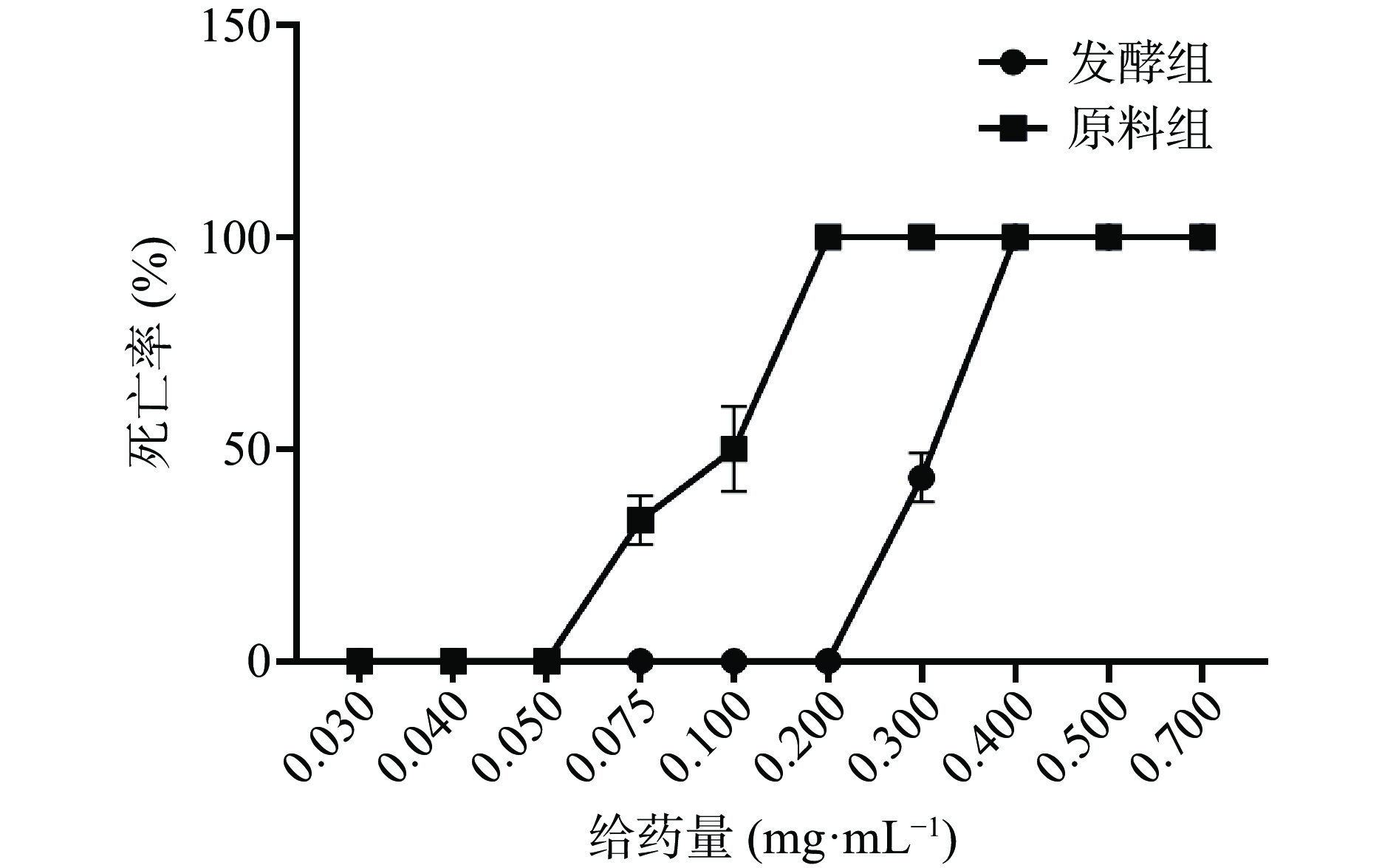
2.2.1 斑马鱼急性毒性结果
桑寄生茶发酵样的毒性较原料样明显降低。如图1所示,发酵组样品在浓度为0.200 mg·mL−1时达到LC0,而原料组LC0最大浓度为0.050 mg·mL−1,明显低于发酵组。选取两组样品均为LC0的最大浓度0.05 mg·mL−1作为给药浓度。
2.2.2 发酵前后桑寄生茶对NAFLD模型斑马鱼的保护作用
“0.1%蛋黄粉+5 mmol·mL−1硫代乙酰胺”模型较空白组,TC、TG、LDL-C、AST、ALT等各生化指标均有显著性差异(P<0.05),即模型组达到NAFLD模型标准。与模型组相比,阿托伐他汀组与发酵组各生化指标均有显著性差异(P<0.05),即有明显的降血脂及抑制肝脏损伤功效。原料组中TC、TG与模型组无显著性差异(P>0.05),而在LDL-C、AST、ALT等生化指标中出现显著性差异(P<0.01),其结果符合传统认知中桑寄生“补肝肾”的功效特点,但其“补肝肾”功效与脂质代谢之间关系不显著。各组生化指标结果见表9。
表 9 发酵前后桑寄生茶对NAFLD模型斑马鱼生化指标的影响(n=5)Table 9. Influence of Taxilli Herba tea before and after fermentation on biochemical parameters of zebrafish NAFLD model组别 TC(mmol·gprot−1) TG(mmol·gprot−1) LDL-C(mmol·gprot−1) AST(U·gprot−1) ALT(U·gprot−1) 空白组 0.08±0.01 0.04±0.01 0.13±0.02 129.01±9.31 29.75±3.22 模型组 0.09±0.01* 0.07±0.01** 0.14±0.01* 154.38±4.53** 32.48±2.20* 阿托伐他汀组 0.07±0.01## 0.05±0.01## 0.12±0.01## 139.94±11.90## 28.78±3.21## 发酵组 0.07±0.01## 0.06±0.01# 0.13±0.01## 132.70±8.73## 29.45±3.70# 原料组 0.09±0.01 0.07±0.01 0.12±0.01## 134.15±10.34## 27.53±2.25## 注:与空白组相比:*P<0.05, **P<0.01;与模型组相比: #P<0.05, ##P<0.01。 2.3 UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS差异代谢物分析
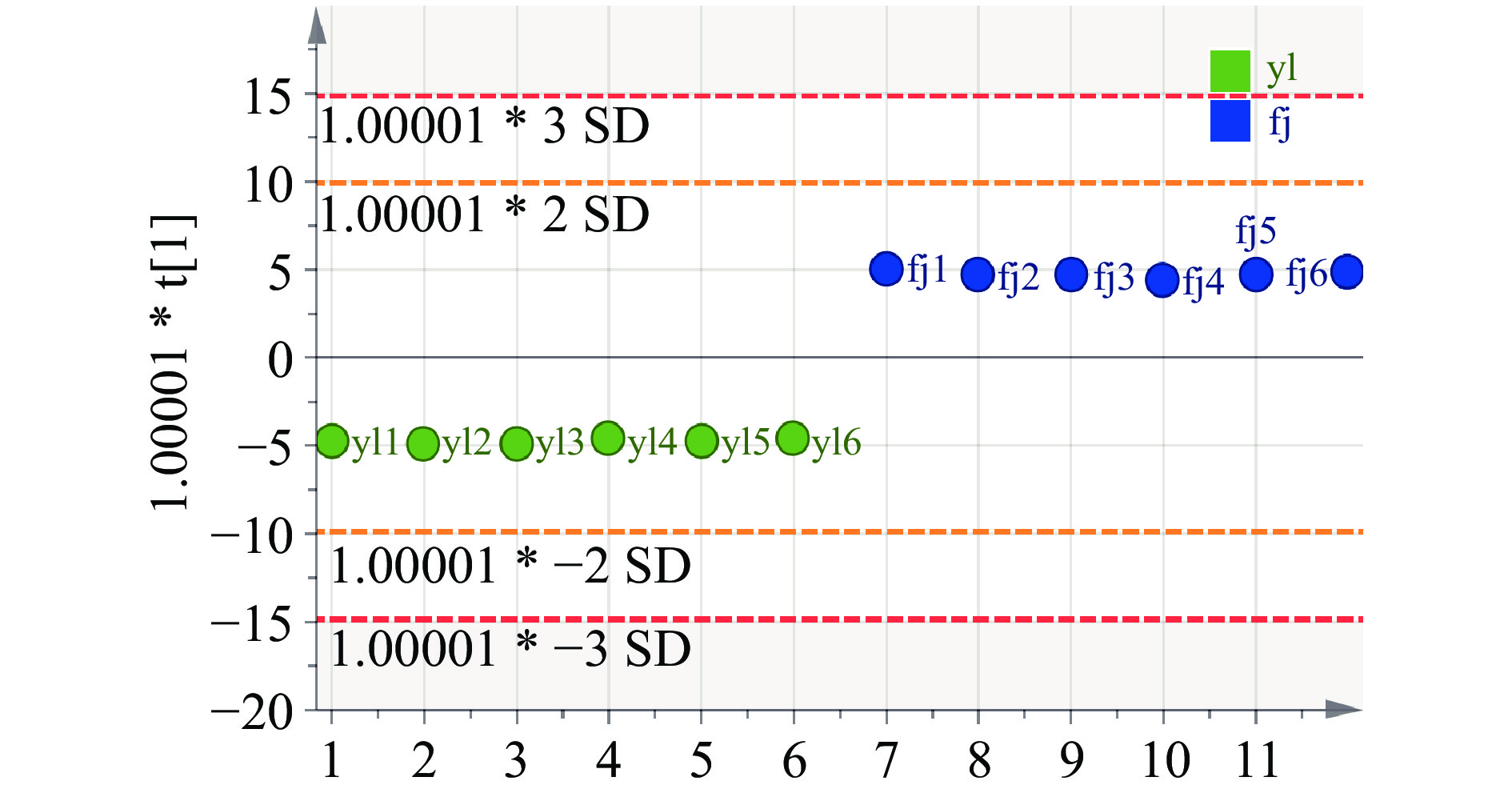
通过UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS检测冠突曲霉发酵前后桑寄生茶样品,共得到32种化学成分,将32种化合物及其峰面积信息代入SIMCA 14.1进行OPLS-DA分析。交叉验证R2Y和Q2均大于0.9,且R2Y-Q2<0.3,即样品间差异非常显著,如图2所示。通过SIMCA中Permutation进行200次随机改变分类变量Y的排列顺序进行置换检验,如图3所示,R2Y<0.4,且Q2Y<0.05,可排除背景相关,该模型稳健性好,无过拟合现象。
依据OPLS-DA模型得到的VIP值、单因素方差分析结果、FC等筛选条件,共筛选出14种差异代谢物,包含酚酸类6种,黄酮类3种,生物碱3种,鞣质1种,糖类1种,详见表10。其中海胆灵(Echinulin)和新海胆灵A(Neoechinulin A)为发酵后样品的特征性代谢产物,无法计算FC值。
表 10 差异代谢物Table 10. Differential metabolites序号 tR(min) 分子式 准分子离子峰(m/z) VIP FC 化合物 1 1.89 C11H9NO2 188.0709 [M+H]+ 1.14 0.11 3-吲哚丙烯酸 2 5.06 C21H20O11 449.1086[M+H]+ 1.12 0.49 槲皮苷 3 7.62 C19H21N3O2 324.1710[M+H]+ 1.14 − 新海胆灵A 4 14.00 C29H39N3O2 462.312[M+H]+ 1.14 − 海胆灵 5 16.33 C19H28O3 305.2115[M+H]+ 1.14 28.81 灰绿曲霉黄色 6 0.50 C6H12O6 179.0561[M-H]− 1.13 0.48 塔格糖 7 0.51 C6H12O7 195.051[M-H]− 1.13 0.29 葡萄糖酸 8 0.54 C4H6O5 133.0144[M-H]− 1.13 0.30 苹果酸 9 1.11 C13H16O10 331.0673[M-H]− 1.13 0.42 没食子酸 3-O-β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 10 1.61 C7H6O4 153.0194[M-H]− 1.14 2.66 原儿茶酸 11 2.43 C15H14O6 289.0717[M-H]− 1.14 0.38 儿茶素 12 3.21 C14H18O9 329.0883[M-H]− 1.13 0.37 根皮乙酰苯-4'-O-葡萄糖苷 13 4.87 C7H6O3 137.0246[M-H]− 1.14 0.36 水杨酸 14 5.24 C15H12O6 287.0561[M-H]− 1.13 2.69 圣草酚 2.4 基于差异代谢物的网络药理学分析
2.4.1 活性成分与疾病靶点筛选
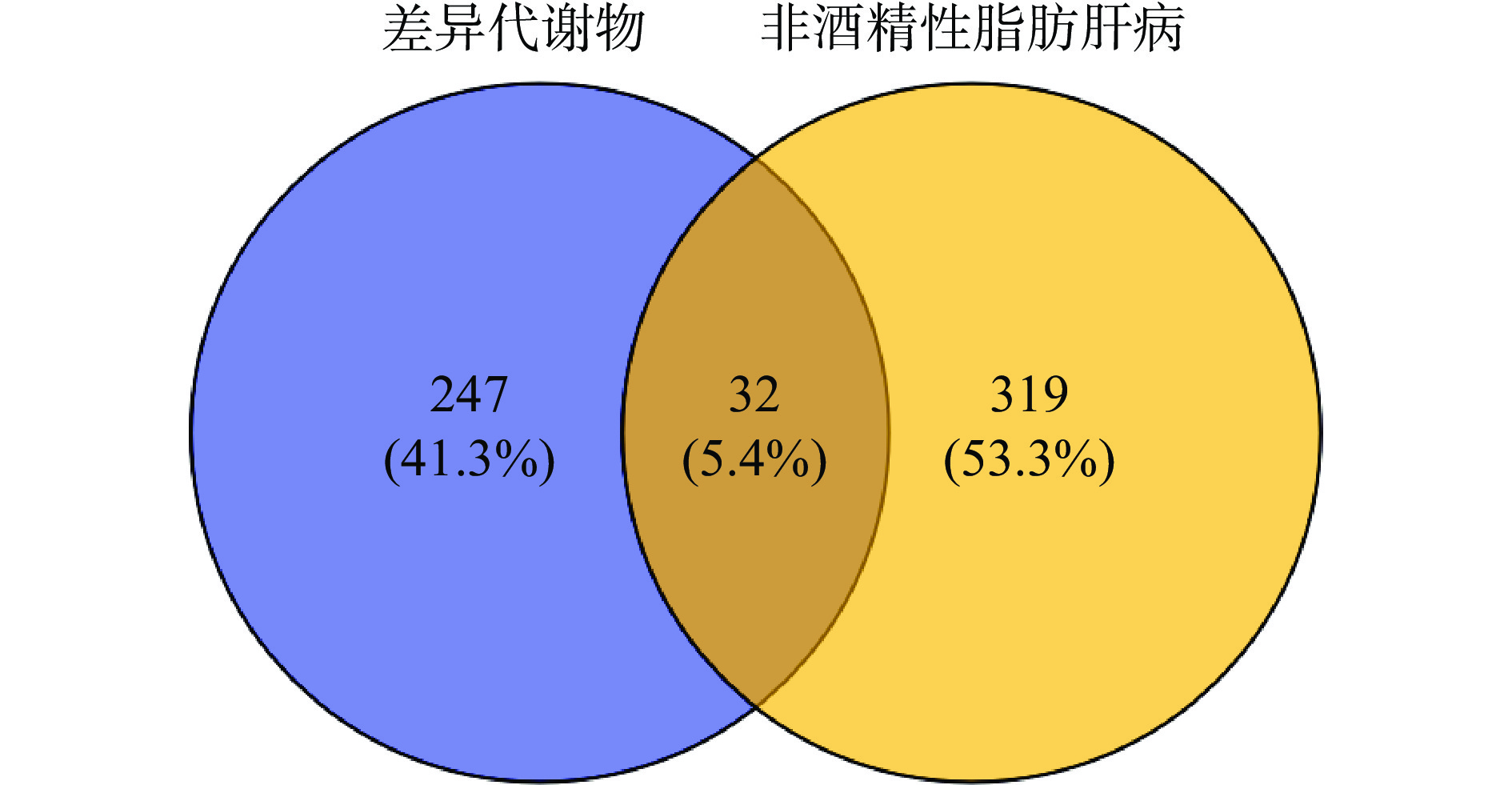
对Drugbank、BindingDB、STITCH、SwissTraget-Prediction平台所查找基因去重后得到279个活性成分靶点。通过genecard收集NAFLD的相关靶点351个。对疾病靶点及成分靶点作靶点映射,筛选出潜在活性靶点32个,如图4所示。
2.4.2 交集靶点PPI网络构建及核心靶点筛选
将32个交集靶点导入String构建蛋白相互作用(PPI)网络,剔除1个无相关作用靶点GCKR,得到由31个节点,144条边所组成的PPI网络,导入Cytoscape 3.9.0进行可视化分析,如图5所示。根据DE、BC、CC等3个拓扑参数进行核心靶点筛选,拓扑参数筛选阈值为均值(DE>9、BC>0.026、CC>0.582),得到7个核心靶点,核心靶点相关信息见表11。
表 11 核心蛋白拓扑参数信息Table 11. Topological parameter information of core proteinProtein Gene Uniprot ID DE CC BC Interleukin 6 IL6 P05231 26 0.882 0.333 Jun Proto-Oncogene, AP-1 Transcription Factor Subunit JUN P05412 19 0.732 0.090 Signal Transducer And Activator Of Transcription 3 STAT3 P40763 17 0.682 0.036 Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor EGFR P00533 17 0.698 0.050 Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthase 2 PTGS2 P35354 16 0.667 0.046 Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 1 Group H Member 4 NR1H4 Q96RI1 11 0.612 0.044 Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor LDLR P01130 11 0.612 0.040 2.4.3 GO分析及KEGG通路富集分析
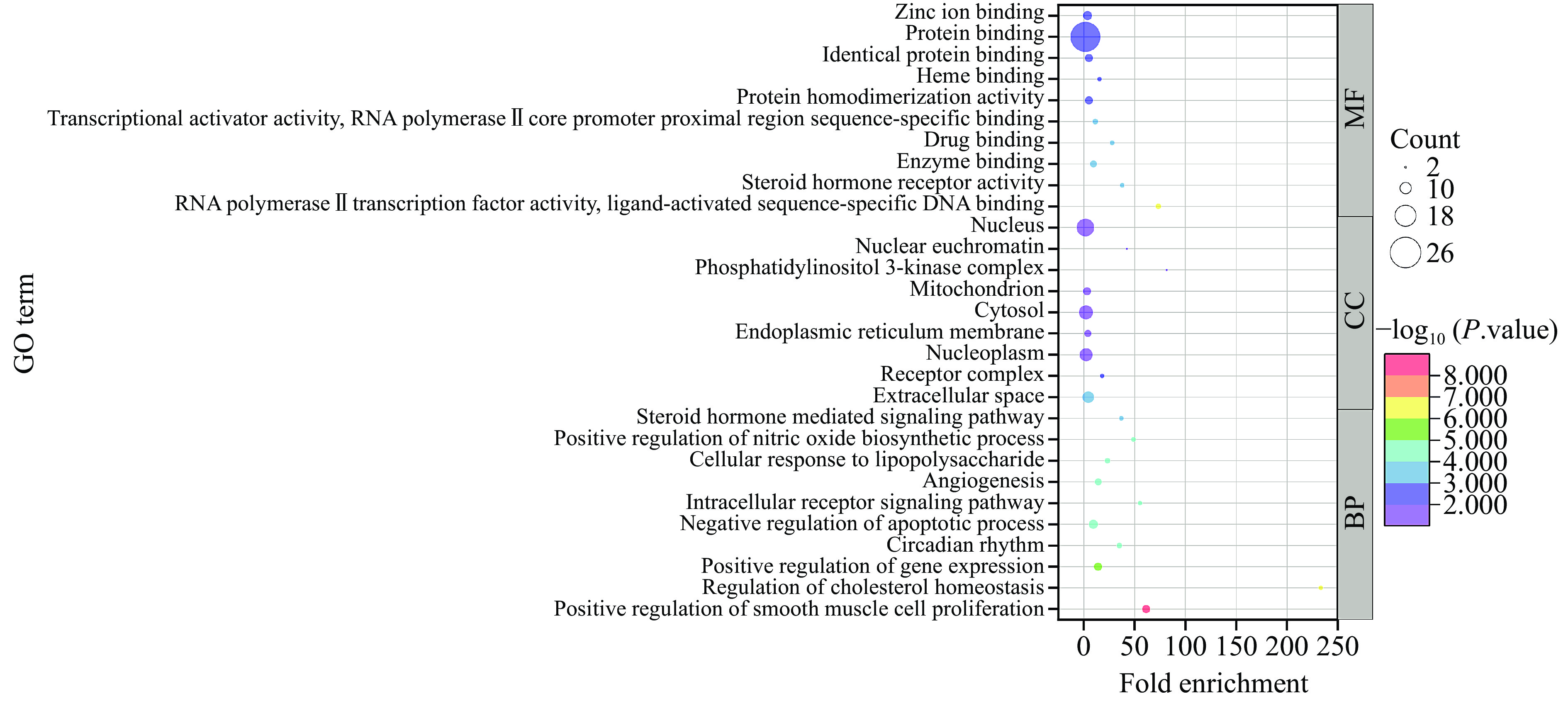
将交集靶点导入DAVID数据库进行GO及KEGG富集分析,P<0.05为条件,筛选得到GO条目124个,其中生物过程(BP)条目94个,细胞组分(CC)条目9个,分子功能(MF)条目21个。分别对生物过程、细胞组分、分子功能组成P值前10的条目进行可视化分析,结果如图6所示。生物过程方面,主要参与细胞的增殖与凋亡,对胆固醇、脂多糖、类固醇激素的调控等;细胞组分方面,与胞外空间、核体、内质网等细胞各个部分均联系密切;分子功能方面,与酶、药物、蛋白质、离子结合,及酶、蛋白质、激酶活性调节等功能有关。结果表明差异代谢物可通过生物学途径防治NAFLD。
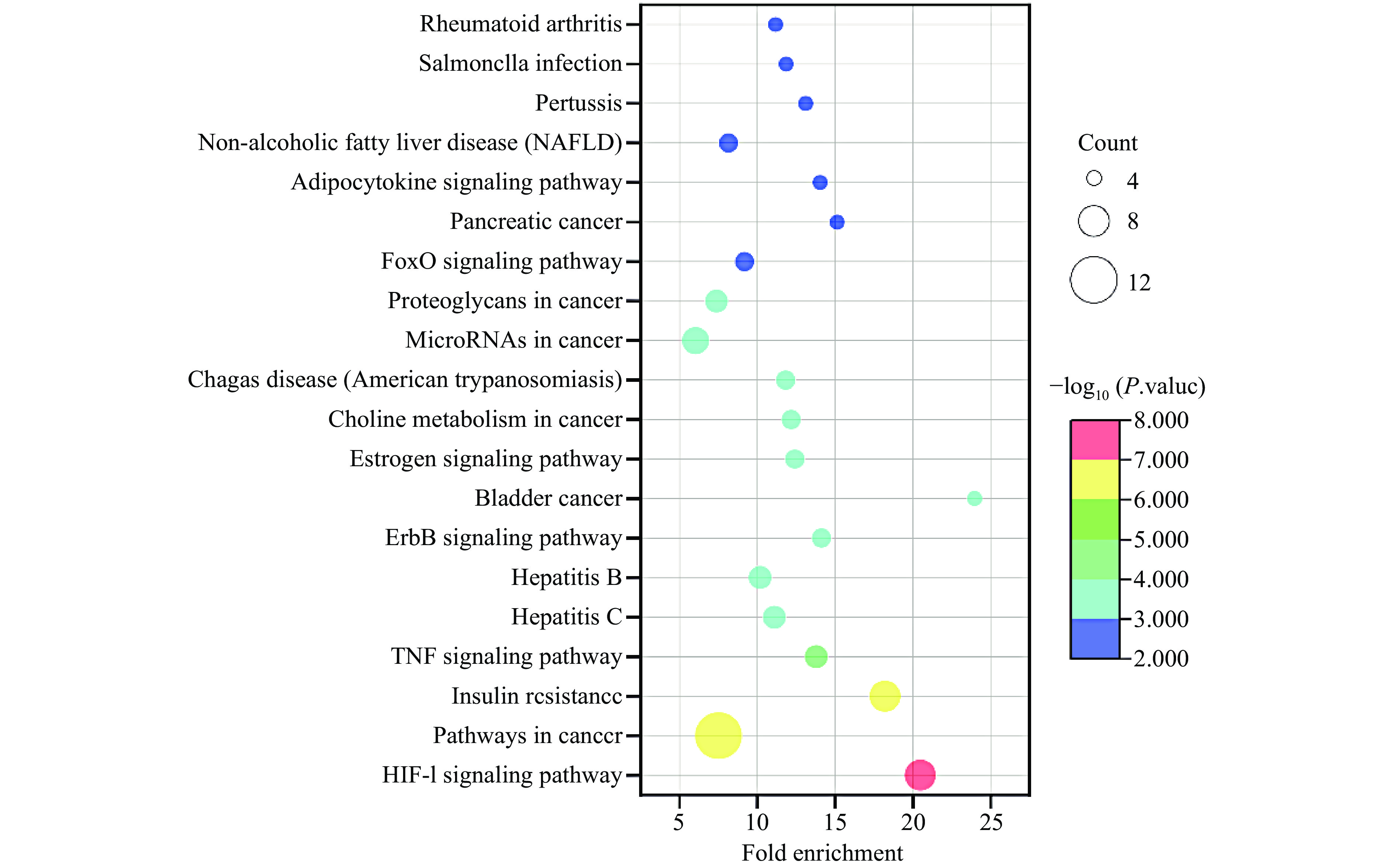
根据筛选条件P<0.05得到KEGG信号通路46条,选取前20条目通路进行可视化分析,如图7所示。其中,HIF-1、癌症、胰岛素抵抗、肿瘤坏死因子信号通路被显著富集,为关键信号通路。此外,肝炎、脂肪细胞因子信号、NAFLD等肝脏功能相关信号通路也被富集,表明差异代谢物能通过多种信号通路发挥对NAFLD的防治作用。
2.4.4 “差异代谢物-靶点-通路-疾病”调控网络的构建
选取14个差异代谢物、32个共同靶点及前20条KEGG信号通路导入Cytoscape 3.9.0构建“差异代谢物-靶点-通路-疾病”网络。该网络共有67个节点,184条相互作用直线。使用Analyze Network网络节点拓扑参数进行关键成分筛选,参数阈值为DE>5,BC>0.023,CC>0.380,得到2个关键成分,海胆灵和新海胆灵A,2个成分均为发酵后的特征性成分。其中,海胆灵作用于3个核心靶点LDLR、JUN、NR1H4,新海胆灵A作用于2个核心靶点EGFR、STAT3,即冠突曲霉发酵工艺能够产生多种成分并通过多种生物途径协同防治NAFLD。如图8。
2.4.5 关键成分和核心靶点的分子对接验证
PPI网络筛选的7个核心靶点与调控网络中2个关键成分按默认参数进行分子对接,结果见表12。除新海胆灵A与JUN基因结合能为-5 kcal·mol−1外,2种关键成分与核心靶点间结合能均<-5 kcal·mol−1,即2种关键成分与7个核心靶点的结合活性较好。
表 12 关键成分与核心靶点的分子对接Table 12. Molecular docking of key compounds and core targets化合物 基因 PDB ID 结合能
(kcal·mol−1)结合位点 海胆灵 IL6 1ALU −7.7 ASP-140, TYR-90 JUN 6Y3V −6.2 ASN-42 STAT3 6NJS −6.3 LYS-658 EGFR 5UG9 −6.5 ARG-776 PTGS2 5F19 −8.6 GLN-327, TRP-323 NR1H4 6HL1 −6.3 ASN-354, PHE-278 LDLR 2FCW −6.1 GLN-104, GLU-269 新海胆灵A IL6 1ALU −5.5 GLN-175 JUN 6Y3V −5.0 GLU-133 STAT3 6NJS −6.2 PRO-333 EGFR 5UG9 −6.5 ALA-955 PTGS2 5F19 −7.6 ARG-44, ARG-61, LYS-546 NR1H4 6HL1 −5.6 LYS-262 LDLR 2FCW −6.1 ARG-111 3. 讨论与结论
胰岛素抵抗、糖尿病、肝损伤、代谢功能异常等是NAFLD发病的独立危险因素及常见伴随表现[28],因此,对于NAFLD的防治需兼顾多类型疾病靶点的调控。
发酵前桑寄生茶相关的核心靶点IL6、PTGS2均与肿瘤坏死因子的调节有关。IL6、PTGS2可通过系统介导肝细胞的凋亡,影响肝炎、急性肝衰竭的发病[29-31]。靶点IL6还参与胰岛素抵抗信号通路的调节,影响肥胖、2型糖尿病、非酒精性脂肪肝等[32-33]的发病。罗泽萍等[34]研究发现桑寄生醇提液具有改善2型糖尿病模型小鼠高血糖水平及肝肾并发症、保护肝肾功能的作用。即桑寄生茶在防治NAFLD方面具有影响糖脂代谢及炎症发生的优势。
冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶的关键成分海胆灵、新海胆灵A可作用于NR1H4、LDLR、JUN、EGFR、STAT3等靶点发挥对NAFLD的防治作用。EGFR靶点作用于糖酵解和葡萄糖的转运,且影响葡萄糖耐量[35]。EGFR还与JUN共同参与ErbB信号通路的调节,进而调节生物反应[36]。STAT3是蛋白酪氨酸激酶(JAk)/信号转导子转录激活子(STAT)的代表性信号传递子,JAk表达低的人群,其肥胖程度较严重[37]。STAT3还与IL6共同参与FoxO信号通路的调节,进而影响葡萄糖代谢、抗氧化应激等细胞生理活动[38]。此外,NR1H4可调控胆汁酸合成[39]、参与脂质代谢;LDLR可调控LDL-C的胞吞作用[40],从而在NAFLD中发挥防治作用。冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶结合了桑寄生茶降血糖、抗炎,以及冠突曲霉代谢产物降血脂、降血糖的优势,为NAFLD的防治提供新的方案。
本研究优选了冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶的加工工艺:含水量35%、渥堆时间3 h、接种量1×106 CFU·mL−1和发酵时间7 d。此条件下的冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶对NAFLD有显著的防治作用,网络药理学推测出关键成分海胆灵、新海胆灵A作用于NR1H4、LDLR、JUN、EGFR、STAT3等核心靶点,在此过程发挥重要作用,为深入研究冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶的药效物质基础和作用机制提供了理论基础,也为冠突曲霉发酵桑寄生茶开发成防治NAFLD的药膳、膳食补充剂等提供参考。
-
表 1 判断矩阵评分
Table 1 Judgment matrix scoring table
评价指标 总黄酮 茶多酚 原花
青素可溶
性糖游离
氨基酸可溶性
蛋白水浸
出物总黄酮 1 2 2 3 4 4 1/2 茶多酚 1/2 1 1 2 2 3 1/3 原花青素 1/2 1 1 1 2 2 1/4 可溶性糖 1/3 1/2 1 1 1 1 1/5 游离氨基酸 1/4 1/2 1/2 1 1 1 1/7 可溶性蛋白 1/4 1/3 1/2 1 1 1 1/8 水浸出物 2 3 4 5 7 8 1 表 2 正交试验各因素水平设置
Table 2 Factors of orthogonal test
水平 因素 含水量(A)
(%)渥堆时间(B)
(h)菌液浓度(C)
(CFU·mL−1)发酵时间(D)
(d)1 25 1 1×105 7 2 30 2 1×106 9 3 35 3 1×107 11 表 3 各指标评分标准
Table 3 Scoring criteria of each index
指标 评价标准 评分 外形 形态美,色泽油润,匀整,净度好,金花茂盛,金黄,颗粒大,分布均匀 90<x≤100 形态有差异,色泽尚油润,较匀整,净度较好,金花较茂盛,黄色,颗粒较大,分布较均匀 80<x≤90 形态差异大,色泽暗,尚匀净,金花小,浅黄色,颗粒小,分布有明显差异 70<x≤80 汤色 根据发酵程度划分红浓、橙红、橙黄、黄绿等档次,明亮,澄清 90<x≤100 根据发酵程度划分红浓、橙红、橙黄、黄绿等档次,尚明亮,略有浑浊 80<x≤90 根据发酵程度划分红浓、橙红、橙黄、黄绿等档次,欠亮,浑浊 70<x≤80 香气 香气纯正,无杂气味,香高爽,香气持久 90<x≤100 香气较高尚纯正,无杂气味 80<x≤90 香气尚纯 70<x≤80 滋味 醇厚,回味甘爽 90<x≤100 尚醇厚 80<x≤90 尚醇,略有苦涩等杂味 70<x≤80 叶底 嫩度匀整,明亮,匀齐 90<x≤100 嫩度尚匀整,明亮,尚匀齐 80<x≤90 嫩度差异大,尚明,欠匀齐 70<x≤80 表 4 正交试验样品主要化学成分百分含量及AHP评分
Table 4 Percentage content of main chemical components and AHP scores of orthogonal test samples
样品 A含水量
(%)B渥堆时间
(h)C菌液浓度
(CFU·mL−1)D发酵时间
(d)总黄酮
(%)茶多酚
(%)原花青素
(%)可溶性糖
(%)游离氨基酸
(%)可溶性蛋白
(%)水浸出物
(%)AHP
评分1 1 1 1 1 1.78±0.00 2.79±0.00 0.17±0.00 2.25±0.00 0.50±0.00 0.48±0.01 19.65±0.05 90.32 2 1 2 2 2 1.68±0.00 2.98±0.00 0.17±0.00 2.20±0.01 0.41±0.00 0.50±0.01 19.99±0.07 89.62 3 1 3 3 3 1.55±0.01 2.86±0.00 0.20±0.00 2.40±0.00 0.45±0.00 0.53±0.00 18.73±0.08 87.66 4 2 1 2 3 1.56±0.01 2.78±0.00 0.17±0.00 2.20±0.02 0.42±0.00 0.47±0.01 18.33±0.05 83.96 5 2 2 3 1 1.68±0.00 2.95±0.00 0.18±0.00 2.43±0.01 0.43±0.00 0.51±0.01 20.36±0.04 91.13 6 2 3 1 2 1.72±0.00 2.87±0.00 0.24±0.00 2.54±0.04 0.45±0.00 0.74±0.01 19.46±0.06 94.10 7 3 1 3 2 1.50±0.02 2.67±0.00 0.14±0.00 2.21±0.02 0.40±0.00 0.51±0.01 18.42±0.07 81.76 8 3 2 1 3 1.52±0.00 2.72±0.00 0.13±0.00 2.25±0.00 0.40±0.00 0.48±0.01 18.86±0.04 82.77 9 3 3 2 1 1.96±0.00 2.70±0.00 0.21±0.00 2.77±0.02 0.48±0.00 0.54±0.01 19.80±0.05 95.32 表 5 方差分析
Table 5 Anova analysis
工艺因素 Ⅲ类平方和 自由度 均方 F值 显著性 含水量 49.903 2 24.951 1649.797 P<0.01 渥堆时间 226.240 2 113.120 7479.560 P<0.01 菌液浓度 38.852 2 19.426 1284.450 P<0.01 发酵时间 249.256 2 124.628 8240.494 P<0.01 注:F0.05(2,2)=19.00;F0.01(2,2)=99.00。 表 6 主要考察指标线性回归方程
Table 6 Linear regression equation of main indexes
考察指标 线性回归方程 线性回归
决定系数R2线性范围
(mg/mL)总黄酮 y=1.25356x+0.0379851 0.9997 0.200~0.800 茶多酚 y=0.0134573x+0.0237366 0.9998 0.010~0.100 原花青素 y=5.95447x−0.0694942 0.9990 0.025~0.250 可溶性糖 y=6.04079x+0.0189998 0.9995 0.025~0.200 游离氨基酸 y=3.60380x−0.251955 0.9994 0.100~0.600 可溶性蛋白 y=4.50928x−0.0141022 1.0000 0.020~0.100 表 7 正交试验样品感官评定结果(n=6)
Table 7 Sensory evaluation results on samples of orthogonal test (n=6)
样品 外形 汤色 香气 滋味 叶底 感官审评得分 评语 评分 评语 评分 评语 评分 评语 评分 评语 评分 1 形态有差异,
分布均匀84.00 橙红,明亮 90.50 香气纯正,香高爽 92.67 醇厚 90.67 嫩度匀整 84.67 89.21 2 形态有差异,
金花较茂盛85.00 橙红,明亮 90.17 香气较高尚纯正 84.50 尚醇厚 88.83 嫩度匀整,明亮,
尚匀齐89.17 87.22 3 形态有差异,
金花较茂盛85.17 橙红,明亮 90.67 香气较高尚纯正 87.67 尚醇厚 88.17 嫩度匀整 82.83 87.28 4 形态有差异 83.33 红浓,明亮 91.33 香气较高尚纯正 89.67 尚醇厚,尚甘爽 89.50 嫩度匀整,明亮,
尚匀齐89.17 88.55 5 形态有差异 83.00 橙黄,尚明亮 88.67 香气较高尚纯正 88.83 尚醇厚,尚甘爽 89.17 嫩度匀整,明亮,
尚匀齐88.17 87.68 6 形态有差异 83.67 橙黄,尚明亮 86.50 香气较高尚纯正 85.33 尚醇厚 87.83 嫩度匀整,尚匀齐 85.17 85.91 7 形态有差异,金花较茂盛,分布较均匀 85.83 橙黄,尚明亮 86.67 香气较高尚纯正 85.17 尚醇厚,略涩 83.76 嫩度匀整,明亮,
匀齐91.00 85.66 8 形态有差异,分布均匀 84.33 橙黄,尚明亮 86.83 香气较高尚纯正 88.83 尚醇厚,略涩 84.17 嫩度匀整 82.83 85.63 9 形态有差异,金花较茂盛,分布较均匀 85.33 橙黄,尚明亮 84.17 香气较高尚纯正 87.83 尚醇厚 88.17 嫩度匀整 84.17 86.52 表 8 正交试验样品综合评分结果
Table 8 Comprehensive evaluation on samples of orthogonal test
样品 AHP化学成分得分 感官审评得分 总分 1 90.32 89.21 89.77 2 89.62 87.22 88.42 3 87.66 87.28 87.47 4 83.96 88.55 86.26 5 91.13 87.68 89.40 6 94.10 85.91 90.00 7 81.76 85.66 83.71 8 82.77 85.63 84.20 9 95.32 86.52 90.92 表 9 发酵前后桑寄生茶对NAFLD模型斑马鱼生化指标的影响(n=5)
Table 9 Influence of Taxilli Herba tea before and after fermentation on biochemical parameters of zebrafish NAFLD model
组别 TC(mmol·gprot−1) TG(mmol·gprot−1) LDL-C(mmol·gprot−1) AST(U·gprot−1) ALT(U·gprot−1) 空白组 0.08±0.01 0.04±0.01 0.13±0.02 129.01±9.31 29.75±3.22 模型组 0.09±0.01* 0.07±0.01** 0.14±0.01* 154.38±4.53** 32.48±2.20* 阿托伐他汀组 0.07±0.01## 0.05±0.01## 0.12±0.01## 139.94±11.90## 28.78±3.21## 发酵组 0.07±0.01## 0.06±0.01# 0.13±0.01## 132.70±8.73## 29.45±3.70# 原料组 0.09±0.01 0.07±0.01 0.12±0.01## 134.15±10.34## 27.53±2.25## 注:与空白组相比:*P<0.05, **P<0.01;与模型组相比: #P<0.05, ##P<0.01。 表 10 差异代谢物
Table 10 Differential metabolites
序号 tR(min) 分子式 准分子离子峰(m/z) VIP FC 化合物 1 1.89 C11H9NO2 188.0709 [M+H]+ 1.14 0.11 3-吲哚丙烯酸 2 5.06 C21H20O11 449.1086[M+H]+ 1.12 0.49 槲皮苷 3 7.62 C19H21N3O2 324.1710[M+H]+ 1.14 − 新海胆灵A 4 14.00 C29H39N3O2 462.312[M+H]+ 1.14 − 海胆灵 5 16.33 C19H28O3 305.2115[M+H]+ 1.14 28.81 灰绿曲霉黄色 6 0.50 C6H12O6 179.0561[M-H]− 1.13 0.48 塔格糖 7 0.51 C6H12O7 195.051[M-H]− 1.13 0.29 葡萄糖酸 8 0.54 C4H6O5 133.0144[M-H]− 1.13 0.30 苹果酸 9 1.11 C13H16O10 331.0673[M-H]− 1.13 0.42 没食子酸 3-O-β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 10 1.61 C7H6O4 153.0194[M-H]− 1.14 2.66 原儿茶酸 11 2.43 C15H14O6 289.0717[M-H]− 1.14 0.38 儿茶素 12 3.21 C14H18O9 329.0883[M-H]− 1.13 0.37 根皮乙酰苯-4'-O-葡萄糖苷 13 4.87 C7H6O3 137.0246[M-H]− 1.14 0.36 水杨酸 14 5.24 C15H12O6 287.0561[M-H]− 1.13 2.69 圣草酚 表 11 核心蛋白拓扑参数信息
Table 11 Topological parameter information of core protein
Protein Gene Uniprot ID DE CC BC Interleukin 6 IL6 P05231 26 0.882 0.333 Jun Proto-Oncogene, AP-1 Transcription Factor Subunit JUN P05412 19 0.732 0.090 Signal Transducer And Activator Of Transcription 3 STAT3 P40763 17 0.682 0.036 Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor EGFR P00533 17 0.698 0.050 Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthase 2 PTGS2 P35354 16 0.667 0.046 Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 1 Group H Member 4 NR1H4 Q96RI1 11 0.612 0.044 Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor LDLR P01130 11 0.612 0.040 表 12 关键成分与核心靶点的分子对接
Table 12 Molecular docking of key compounds and core targets
化合物 基因 PDB ID 结合能
(kcal·mol−1)结合位点 海胆灵 IL6 1ALU −7.7 ASP-140, TYR-90 JUN 6Y3V −6.2 ASN-42 STAT3 6NJS −6.3 LYS-658 EGFR 5UG9 −6.5 ARG-776 PTGS2 5F19 −8.6 GLN-327, TRP-323 NR1H4 6HL1 −6.3 ASN-354, PHE-278 LDLR 2FCW −6.1 GLN-104, GLU-269 新海胆灵A IL6 1ALU −5.5 GLN-175 JUN 6Y3V −5.0 GLU-133 STAT3 6NJS −6.2 PRO-333 EGFR 5UG9 −6.5 ALA-955 PTGS2 5F19 −7.6 ARG-44, ARG-61, LYS-546 NR1H4 6HL1 −5.6 LYS-262 LDLR 2FCW −6.1 ARG-111 -
[1] 尚玮璇, 刘璐, 雷素珍, 等. 功能性碳水化合物通过调节肠道菌群和代谢物改善非酒精性脂肪肝的作用机制[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(14):311−318. [SHANG W X, LIU L, LEI S Z, et al. Improvement effect of functional carbohydrates on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating intestinal flora and metabolites[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(14):311−318. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.029741 [2] MUNDI M S, VELAPATI S, PATEL J, et al. Evolution of NAFLD and its management[J]. Nutr Clin Pract,2020,35(1):72−84. doi: 10.1002/ncp.10449
[3] LI J, ZOU B, YEO Y H, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999-2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol,2019,4(5):389−398. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30039-1
[4] ESTES C, ANSTEE Q M, ARIAS-LOSTE M T, et al. Modeling NAFLD disease Burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016-2030[J]. Journal of Hepatology,2018,69(4):896−904. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.036
[5] 宋子羽, 秦虹, 郑温雅. 环状RNA与非酒精性脂肪肝疾病的研究进展[J]. 中国药理学通报,2021,37(10):1338−1342. [SONG Z Y, QIN H, ZHENG W Y. Recent advence in understanding relationship between circRNAs and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin,2021,37(10):1338−1342. [6] DAI X, FENG J, CHEN Y, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Molecular insights and therapeutic perspectives[J]. Chin Med,2021,16(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00469-4
[7] 何克谏. 生草药性备要[M]. 广州: 广东科技出版社, 2009: 57. HE Kejian. Preparation of raw herbal medicine[M]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Science and Technology Press, 2009: 57.
[8] 巫文鑫, 李斌, 刘小勇, 等. 寄生茶研究现状与发展前景[J]. 中国农学通报,2021,37(34):141−146. [WU W X, LI B, LIU X Y, et al. The current situation and prospect of Jisheng Tea[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2021,37(34):141−146. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0698 [9] GE Y, WANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Comparative genomic and transcriptomic analyses of the Fuzhuan brick tea-fermentation fungus Aspergillus cristatus[J]. BMC Genomics,2016,17:428. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2637-y
[10] KONG W, HUANG C, SHI J, et al. Recycling of Chinese herb residues by endophytic and probiotic fungus Aspergillus cristatus CB10002 for the production of medicinal valuable anthraquinones[J]. Microb Cell Fact,2019,18(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12934-019-1150-9
[11] LEE S, REDDY C K, RYU J J, et al. Solid-state fermentation with Aspergillus cristatus enhances the protopanaxadiol- and protopanaxatriol-associated skin anti-aging activity of Panax notoginseng[J]. Front Microbiol,2021,12:602135. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.602135
[12] XIE Z, BAI Y, CHEN G, et al. Modulation of gut homeostasis by exopolysaccharides from Aspergillus cristatus (MK346334), a strain of fungus isolated from Fuzhuan brick tea, contributes to immunomodulatory activity in cyclophosphamide-treated mice[J]. Food Funct,2020,11(12):10397−10412. doi: 10.1039/D0FO02272A
[13] XIE Z, BAI Y, CHEN G, et al. Immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharides from the mycelium of Aspergillus cristatus, isolated from Fuzhuan brick tea, associated with the regulation of intestinal barrier function and gut microbiota[J]. Food Res Int,2022,152:110901. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110901
[14] 王成, 龚莉虹, 郭朝成, 等. 模式生物斑马鱼在中药药效物质筛选中的应用进展[J]. 中草药,2019,50(24):6125−6134. [WANG C, GONG L H, GUO C C, et al. Application progress on model organism zebrafish in screening of pharmacodynamic substances of Chinese materia medica[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2019,50(24):6125−6134. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.24.030 [15] WANG Y D, YANG J, LI Q, et al. UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS analysis of Seco-Sativene sesquiterpenoids to detect new and bioactive analogues from plant Pathogen Bipolaris sorokiniana[J]. Front Microbiol,2022,13:807014. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.807014
[16] ZHANG R, ZHU X, BAI H, et al. Network pharmacology databases for Traditional Chinese Medicine: Review and assessment[J]. Front Pharmacol,2019,10:123. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00123
[17] ZHANG Y R, LIU Y R, TANG Z S, et al. Rheum officinale Baill. Treats zebrafish embryo thrombosis by regulating NOS3 expression in the arginine biosynthesis pathway[J]. Phytomedicine,2022,99:153967. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.153967
[18] 张娇, 蒋倩倩, 张伯言, 等. 基于AHP-CRITIC法正交优选乌甘袋泡茶提取工艺及抗炎作用研究[J]. 中草药,2020,51(8):2177−2184. [ZHANG J, JIANG Q Q, ZHANG B Y, et al. Study on extraction process and anti-inflammatory effect of Wugan Tea based on AHP-CRITIC analysis[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2020,51(8):2177−2184. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.08.026 [19] 黄蜚颖. 基于寄主影响的中药桑寄生药性研究[D]. 南宁: 广西中医药大学, 2018. HUANG F Y. Study on the difference of cold and hot property of Taxillus chinensis based on host plants[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, 2018.
[20] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 8313-2018 茶叶中茶多酚和儿茶素类含量的检测方法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 8313-2018 Determination of total polyphenols and catechins content in tea[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018.
[21] 天津市市场监督管理委员会. DB12/T 885-2019 植物提取物中原花青素的测定紫外/可见分光光度法[S]. 天津: 天津市地方标准, 2019. Tianjin Administration for Market Regulation. DB12/T 885-2019 Determination of polysaccharide in Lily Bulbus-UV/VIS spectrophotometry[S]. Tianjin: Local Standards of Tianjin, 2019.
[22] 李远华. 茶学综合实验[M]. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2018: 198-199. LI Y H. Comprehensive experiment of tea science[M]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2018: 198-199.
[23] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.124-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中氨基酸的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 5009.124-2016 National food safety standard. Determination of amino acids[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017.
[24] 张馨宇. 杜仲叶功能茶加工工艺研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2016: 14. ZHANG X Y. A study on tea processing technology of Eucommia ulmoides function at tea[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2016: 14.
[25] 国家食品药品监督管理总局, 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB/T 8305-2013 茶 水浸出物测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2013. State Food and Drug Administration, National Health and Family Planning Commission. GB/T 8305-2013 Determination of tea water extract[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2013.
[26] 中华全国供销合作总社杭州茶叶研究院. GB/T 23776-2018 茶叶感官审评方法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. Hangzhou Tea Research Institute of all China Federation of Supply and Marketing Cooperation. GB/T 23776-2018 Methodology for sensory evaluation of tea[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2018.
[27] DONG Y, ZHAO Q, WANG Y. Network pharmacology-based investigation of potential targets of astragalus membranaceous-angelica sinensis compound acting on diabetic nephropathy[J]. Sci Rep,2021,11(1):19496. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98925-6
[28] PAFILI K, RODEN M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) from pathogenesis to treatment concepts in humans[J]. Mol Metab,2021,50:101122. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101122
[29] 马雅斌, 李语玲, 张津. 熊去氧胆酸联合S-腺苷蛋氨酸对药物性肝损伤患者肝功能、Nrf2抗氧化、炎症反应的影响[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志,2018,17(24):2606−2610. [MA Y B, LI Y L, ZHANG J. Influence of ursodeoxycholic acid combined with s-adenosine methionine on liver function, Nrf2 antioxidant and inflammatory response in patients with drug-induced liver injury[J]. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine,2018,17(24):2606−2610. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2018.24.009 [30] 裴燕燕, 毛德文, 王明刚, 等. 解毒化瘀颗粒对急性肝衰竭大鼠OX62、Fas及TNFR1表达的影响[J]. 广州中医药大学学报,2018,35(3):471−476. [PEI Y Y, MAO D W, WANG M G, et al. Effect of Jiedu Huayu Granules on OX62, Fas and TNFR1 Expression in rats with acute hepatic failure[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2018,35(3):471−476. doi: 10.13359/j.cnki.gzxbtcm.2018.03.020 [31] SHUH M, BOHORQUEZ H, LOSS GE JR, et al. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α: Life and death of hepatocytes during liver ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Ochsner J,2013,13(1):119−30.
[32] MUOIO D M, NEWGARD C B. Obesity-related derangements in metabolic regulation[J]. Annu Rev Biochem,2006,75:367−401. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142512
[33] CHOI K, KIM Y B. Molecular mechanism of insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes[J]. Korean J Intern Med,2010,25(2):119−29. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2010.25.2.119
[34] 罗泽萍, 李丽, 潘立卫, 等. 桑寄生醇提物改善2型糖尿病模型小鼠血糖水平及其肝肾并发症的作用及机制研究[J]. 中国药房,2019,30(6):796−801. [LUO Z P, LI L, PAN L W, et al. Improvement effects of ethanol extract from Taxillus sutchuenensis on blood glucose level, liver and renal complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus model mice and its mechanism[J]. China Pharmacy,2019,30(6):796−801. [35] CHOUNG S, KIM J M, JOUNG K H, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in diet-induced obese mice[J]. PLoS One,2019,14(2):e0210828. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210828
[36] HOLBRO T, HYNES NE. ErbB receptors: Directing key signaling networks throughout life[J]. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol,2004,44:195−217. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.44.101802.121440
[37] 梁钰华, 李志家, 邓晓冬, 等. 铁皮石斛联合二甲双胍对2型糖尿病合并非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠的改善作用和机制研究[J]. 现代医学与健康研究电子杂志,2021,5(24):24−28. [LIANG Y H, LI Z J, DENG X D, et al. Effects and mechanisms of Dendrobium candidum combined with metformin on type 2 diabetes mellitus and nonalcoholic fatty liver in mice[J]. Medicine and Health Research,2021,5(24):24−28. [38] GLAUSER DA, SCHLEGEL W. The emerging role of FOXO transcription factors in pancreatic beta cells[J]. J Endocrinol,2007,193(2):195−207. doi: 10.1677/JOE-06-0191
[39] 蔡兆伟, 吕建敏, 凌云, 等. 雄激素缺乏对高脂高胆固醇饲喂小型猪肝mRNA可变剪接的影响[J]. 中国实验动物学报,2018,26(4):424−430. [CAI Z W, LÜ J M, LING Y, et al. Testosterone dificiency regulates mRNA alternative splicing in the liver of miniature pigs fed a high-fat and high-cholesterol diet[J]. Acta Laboratorium Animalis Scientia Sinica,2018,26(4):424−430. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2018.04.003 [40] 周爱儒, 梁康. 生物化学[M]. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2007: 138-140. ZHOU A R, LIANG K. Biochemistry[M]. Beijing: Peking University Medical Press, 2007: 138-140.





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



