Discrimination Analysis of Conventional Baijiu-making Sorghum from Southwest China and Hybrid Sorghum Based on Physicochemical Properties and Metabolomics
-
摘要: 为分析杂交高粱与西南地区常规酿酒高粱成分的差异,建立品种判别方法。本文测定了29个高粱样品的基本理化组分,采用超高效液相色谱-复合四极杆轨道阱质谱法(ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with Q Exactive HF-X mass spectrometry,UHPLC-Q Exactive HF-X-MS)分析不同品种类别高粱的代谢物组成,通过主成分分析(principal component analysis,PCA)、正交偏最小二乘判别分析(orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis,OPLS-DA)模型、聚类分析和受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线分析等统计学方法对理化组分和所有代谢物进行特征成分筛选和品种鉴别模型构建。结果表明西南地区常规品种的支链淀粉和单宁含量比杂交品种高,直链淀粉含量和千粒重偏低,基于理化性质可实现部分样品的鉴别。以全部1048个代谢物为变量构建OPLS-DA模型,筛选出46种主要差异代谢物,重新构建了高粱品种OPLS-DA判别模型,判别准确率达到100%。西南地区常规品种中多种酚类化合物含量相对较高。另外,基于ROC分析和质控样本(quality control sample,QC)的相对标准偏差(relative standard deviation,RSD)进一步筛选出20个诊断准确性较高且重现性较好的差异代谢物。其中丁香亭-3-葡萄糖苷和6''-O-乙酰大豆苷在常规高粱品种中具有更高的表达丰度,D-葡萄糖酸、腐胺、N-乙酰腐胺和L-谷氨酰胺在杂交高粱中含量更高。本研究揭示了西南地区常规酿酒高粱与杂交高粱的差异性,建立的基于UHPLC-Q Exactive HF-X-MS的非靶向代谢组学方法能科学准确地用于高粱品种鉴别,为高粱品种鉴别提供一种新策略。Abstract: The objective of this paper was to analyze the difference of composition between hybrid sorghum and conventional sorghum in southwest China, and to establish the method of variety identification. The basic physical and chemical components of 29 sorghum samples were determined, and the metabolite composition of 29 sorghum samples was determined by ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with Q Exactive HF-X mass spectrometry. The marker component screening and construction of variety identification model were carried out using stoichiometry, which included principal component analysis (PCA), orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA), cluster analysis and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. The model was based on the basic physicochemical composition and all metabolites. The results showed that the contents of amylopectin and tannin of the conventional varieties form southwest China were higher than that of hybrid varieties, while the contents of amylose and 1000-grain weight were lower. By analyzing the physicochemical properties, it was possible to identify certain samples. The OPLS-DA model was constructed with all 1048 compounds variables, and 46 of the differential metabolites that had a significant impact on the model identification were screened out. A novel OPLS-DA identification model was developed for sorghum varieties, achieving a 100% accuracy in identification. The conventional varieties from southwest China exhibited a relatively high concentration of phenolic compounds. Furthermore, after conducting receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and assessing the relative standard deviation (RSD) of quality control sample (QC), 20 feature components that exhibited both high diagnostic accuracy and good reproducibility were identified. Among them, syringetin 3-glucoside and 6"-o-acetyldaidzein had higher expression abundance in conventional sorghum varieties, while D-glucarate, putsutrine, N-acetylputsutrine and L-glutamine had higher content in hybrid sorghum varieties. This study unveiled the disparity in metabolites between hybrid sorghum and conventional sorghum. The study successfully developed a scientifically rigorous and precise untargeted metabolomics approach using UHPLC-Q Exactive HF-X-MS. This method can be effectively utilized for the identification of sorghum varieties, offering a novel strategy for sorghum variety identification.
-
高粱(Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench),又称蜀黍、芦祭、红粱等,是白酒生产的重要原料,其品质优劣对酿酒过程起决定性的作用,并直接影响成品酒的质量[1]。西南地区盛产白酒,因此逐渐形成了以四川和贵州为代表的南方高粱产区。高粱品种繁多,从育种上分为常规品种和杂交品种[2]。杂交高粱是用两个不同的优良高粱品种进行杂交产生杂交种,再由这个杂交种子生长出来的高粱[3]。虽然杂交高粱因其产量高、抗逆性强在全国大面积推广种植,但是西南地区名优酒企多以当地种植的常规品种高粱为酿酒原料。这些常规高粱一般从早期地方品种选育而出,目前常见的品种有国窖红1号、青壳洋、红缨子、泸州红1号、宜糯红和郎糯红等[4]。随着中国白酒酿造行业的深度调整,近年来西南酒企对常规酿酒高粱的需求量很大。但是在实际收粮过程中,一些商贩将当地或其它地区的杂交高粱混入其中,这不利于白酒的品质保障,因此如何鉴别高粱品种的真伪是酒企原料收购中需要解决的重要问题。
目前酒企常用的方法有感官评价,该方法需要工作人员有丰富的经验,同时存在一定主观性,难以形成统一的标准;另外在理化检测方面,现有研究主要集中在比较南方高粱与北方高粱之间的差异分析,鲜有针对杂交高粱与西南地区常规高粱之间的系统比较分析。袁蕊等[5]基于3种南方高粱和3种北方高粱比较得出其中川南产的2种常规品种(国窖红1号和青壳洋)支链淀粉、脂肪和单宁含量较高。卫永太等[6]以中国高粱品种资源目录中记载的8个生态区的2045份中国高粱种质资源数据进行分析发现南方高粱单宁含量普遍高于北方地区。另有研究表明红缨子高粱相较于杂交高粱品种晋202、辽15、辽18和辽7高粱皮厚、单宁含量高[7]。现有研究中关于西南地区常规高粱的特性报道主要是在基本理化层面,没有对内在成分更深入的分析。
随质谱技术与化学计量学方法有新的发展,非靶向代谢组学广泛应用于食品认证领域,如小麦[8]、茶叶[9]和高粱[10]等植物的品种鉴别和差异分析。非靶向代谢组学具有高通量、高灵敏度等优势,能够最大限度覆盖代谢物,无偏向性地对所有代谢小分子进行检测分析,特别是传统检测技术无法检测到的微量成分。Zhou等[11]采用基于LC-ESI-MS/MS的非靶向代谢组学结合多元统计分析了3个不同颜色的甜高粱品种籽粒的代谢谱,发现一些与高粱颜色相关的代谢物。Ramalingam等[12]通过非靶向气相色谱-质谱(GC-MS/MS)分析,对61个不同生长环境(温带和热带)和籽粒颜色的高粱品种进行了植物化学物质的差异研究。倪德让[10]通过气相色谱-质谱联用技术测定酿酒高粱中挥发性物质,以检测到的挥发性物质及对应的相对含量建立PLS-DA判别模型,可以对“红缨子”高粱品种进行准确鉴别。目前,基于LC-MS的非靶向代谢组学方法鲜用于探索不同品种类别的中国酿酒高粱化学特征代谢物。因此本研究旨在以基本理化性质鉴别西南地区常规高粱的基础上,建立一种基于超高效液相色谱-复合四极杆轨道阱质谱的酿酒高粱鉴别方法,同时探索西南地区常规高粱与其它杂交高粱的内在非挥发代谢组分差异,为常规酿酒高粱的品种鉴别提供新的途径。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
收集杂交高粱20份,西南地区常规酿酒高粱共9份,每份样品设三个重复。常规高粱样本均取自于四川,杂交高粱取自四川和山西两地。每个品种选取无机械损伤、无霉变和大小一致的种子,分析检测前保存于−80 ℃冰箱。具体样品信息见表1;甲酸 色谱纯,德国CNW公司;纯水(质谱级)、乙腈(色谱纯)、甲醇(色谱纯) 美国Fisher Chemical公司;2-丙醇 色谱纯,德国Merck公司;2-氯- L -苯丙氨酸 纯度≥98%,瑞士Adamas-beta公司。
表 1 高粱样品信息Table 1. Information of the sorghum samples tested in this study编号 品种名称 类别 编号 品种名称 类别 1 红缨子 常规 16 汉青1号 杂交 2 青壳洋 17 红糯13号 3 国窖红1号 18 瑞杂1号 4 宜糯红4号 19 齐杂7号 5 郎糯红19号 20 吉杂210 6 水儿红 21 红茅6号 7 青壳洋 22 晋杂22号 8 国窖红1号 23 晋杂23 9 泸州红1号 24 冀酿4号 10 兴颗3
杂交25 国酿红235 11 金糯粱6号 26 晋杂22号 12 机糯粱1号 27 凤杂18号 13 齐杂104 28 凤杂4号 14 内杂5号 29 东梁80 15 齐糯115 Vanquish Horizon超高效液相色谱仪、Q Exactive HF-X质谱仪 美国Thermo Scientific公司;ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3色谱柱 美国Waters公司;MS105DU电子天平 瑞士梅特勒托利多公司;Wonbio-96C样品冷冻研磨仪 上海万柏生物科技有限公司;SBL-10TD 控温超声波清洗机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;5424R、5403R冷冻离心机 德国Eppendorf公司;TPKZ-1作物考种分析系统 浙江托普云农科技股份有限公司;CM-5色差仪 柯尼卡美能达公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 理化指标测定
总淀粉、脂肪、蛋白质、单宁和直链淀粉含量测定参照国标GB 5009.9-2016第二法[13]、国标GB 5009.6-2016第一法[14]、国标GB 5009.5-2016第一法[15]、国标GB/T 15686-2008[16]和国标GB/T 15683-2008[17]。千粒重参照徐晓等[18]采用智能考种分析系统测定。色度值L*、a*、b*值采用色差仪测定。
1.2.2 非靶向代谢组学检测
非靶向代谢组学检测的步骤参考文献[19],将高粱籽粒研磨至粉末状后称取50 mg样品,加入0.4 mL 80%(v/v)甲醇水溶液,内含0.02 mg/mL的L-2-氯苯丙氨酸作为内标。−10 ℃,50 Hz条件下冷冻研磨6 min,5 ℃,40 kHz条件下超声提取30 min,−20 ℃下静置30 min后离心15 min(13000×g,4 ℃),上清液为分析样液;另外,每个样本分别移取20 µL上清液,混合后作为质控样本。在样本分析的过程中,每隔一定分析样本插入一个质控样本以便考察检测过程的稳定性。
采用超高效液相色谱-复合四极杆轨道阱高分辨率质谱测定,色谱柱:ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3(100 mm×2.1 mm,1.8 µm);流动相A:95%水+5%乙腈(含0.1%甲酸),流动相B:47.5%乙腈+47.5%异丙醇+5%水(含0.1%甲酸),柱温40 ℃,进样量2 μL。洗脱梯度:0~3.5 min,0%~24.5%B;3.5~5 min,24.5%~65%B;5~5.5 min,65%~100%B;5.5~7.4 min,100%B;7.4~7.6 min,100%~51.5%B;7.6~7.8 min,51.5%~0%B;7.8~9 min,0%B;9~10 min,0%B。流速设置:0~5.5 min,0.4 mL/min;5.5~7.4 min,0.4~0.6 mL/min;7.4~7.6 min,0.6 mL/min;7.6~7.8 min,0.6~0.5 mL/min;7.8~9 min,0.5~0.4 mL/min;9~10 min,0.4 mL/min。
分别采用正、负离子扫描模式。质量扫描范围70~1050 m/z;加热温度425 ℃;毛细管温度为325 ℃;喷雾电压±3500 V;S-Lens电压50 V;碰撞能20-40-60 eV;鞘气流速50 arb;辅助气流速13 arb;一级分辨率60000;二级分辨率7500。
采用Progenesis QI软件(美国Waters公司)对UHPLC-MS原始数据进行基线过滤、峰识别、积分、保留时间校正、峰对齐后,得到一个含保留时间、质荷比和峰面积的数据矩阵。将MS和MSMS质谱信息与代谢公共数据库HMDB(http://www.hmdb.ca/)、Metlin(https://metlin.scripps.edu/)和LipidBlast以及美吉自建库进行匹配,MS质量误差设置为小于10 ppm,同时根据二级质谱匹配得分鉴定代谢物,筛选搜库得分最高的物质为定性结果,并且要求得分>30[20]。
将鉴定到的代谢物及对应的峰面积上传到美吉云平台(cloud.majorbio.com)进行处理。保留一组样品中非零值80%以上的变量,再使用原始数据中的最小值补空缺值。为减小样品制备和仪器不稳定带来的误差,用总和归一化法对样品质谱峰面积,进行归一化,再删除QC样本中相对标准偏差(RSD)>30%的变量,然后进行lg对数化处理得到相对定量值。以经过上述处理后得到的代谢物及对其相对定量值作统计学分析。
1.3 数据处理
小提琴图采用R语言4.1.1绘制,柱形图采用Excel 2019绘制。主成分分析和OPLS-DA分析与绘图采用SIMCA-P 14.1和ropls(R packages),聚类分析与热图绘制采用scipy(Python)Version1.0.0(通过美吉生物云平台)。ROC分析采用SPSS 20.0。
2. 结果与分析
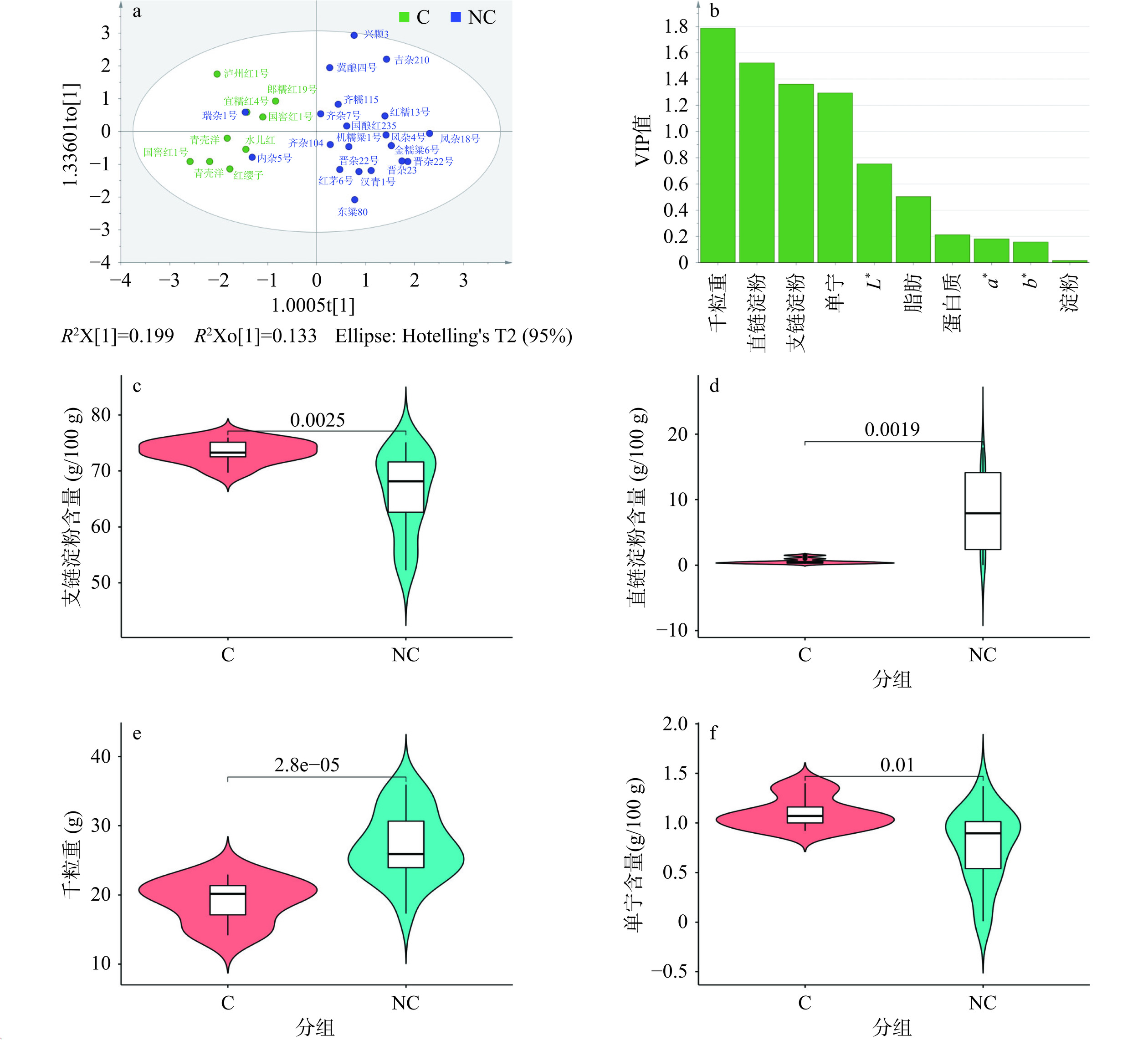
2.1 不同品种高粱的理化性质多元统计分析
首先对多个品种高粱的理化性质进行OPLS-DA分析。如图1a中散点图所示常规高粱和杂交高粱有较好的分离趋势,但有个别杂交高粱品种(内杂5号、瑞杂1号)分布在X轴左侧,与常规高粱距离更近。OPLS-DA模型的累计R2X=0.432,R2Y=0.658,Q2=0.464,具有一定的参考价值。图1 b中以VIP值大于1筛选得出千粒重、直链淀粉、支链淀粉和单宁含量可以作为判别常规高粱的关键理化性质。不同组别高粱的关键理化成分含量及其分布小提琴图如图1c~f所示。小提琴图是箱形图和密度图的结合,主要用来显示数据的分布形状。中间的白色粗条表示四分位数范围,从其延伸的纵向黑线代表理化性质分布的95%置信区间,高度越高,表示组内样本的含量越离散;小提琴的宽度表示当前表达量范围的样本个数,越宽表示此表达量范围的样本分布越多;Y轴表示理化性质的大小;横线上数字为组间差异比较的P值,P<0.05表示差异显著。由图1c~f可知,西南地区常规高粱的支链淀粉和单宁含量显著高于杂交高粱,直链淀粉含量和千粒重显著低于杂交高粱。该结论与以往研究报道相似[5−6],但本研究共选择了7个西南地区常规品种,19个北方或南方的杂交品种,涉及品种更加丰富,可作为西南地区常规酿酒高粱基本理化特性研究的补充。
2.2 不同品种高粱的代谢组学分析
2.2.1 多元统计分析
PCA能够提取原始数据中有效的信息作为新的主成分变量,有效地降低数据维度[21],是一种无监督分析,被广泛应用于代谢组学研究的多变量分析中,以获得众多样本之间的差异概览[22]。经过峰识别和数据预处理,得到的代谢物矩阵包含97个样本(含质控样本,QC)和1048个代谢物及表达丰度(包含正离子和负离子模式下的所有可注释的代谢物)。如图2a所示,得分图中QC样品分布常作为验证代谢组数据集可重复性的一种方法[23]。图2a中QC样品点紧密地聚集在图中心附近,这表明数据采集的质量高。在前两个主成分的得分图中,常规高粱和杂交高粱表现出一定程度的区分,但不是很明显,推测可能是同类品种的酿酒高粱受产地、内在生物学品种的影响产生较大的组内差异。主成分1的方差贡献率为19.07%,主成分2方差贡献率为14.73%,前2个主成分仅反映了所有代谢物33.80%的特征,无法反映整体分散度。因此可进一步采取有监督的多元统计分析方法−正交偏最小二乘判别分析(OPLS-DA)。
运用OPLS-DA可以构建样品与代谢物表达量之间的关系模型,可以放大组间差异,降低组内差异,从而降低不相关差异对数据的影响,对样品进行更好的判别分离[24]。图2b和2c分别是在正离子和负离子模式下进行的OPLS-DA分析,从散点图中可以看出酿酒高粱可以清晰区分开常规高粱和杂交高粱。正离子模式下的OPLS-DA模型由1个预测分量和2个正交分量组成,累计R2X、R2Y和Q2值分别为0.317、0.988和0.979;负离子模式下的OPLS-DA模型由1个预测分量和2个正交分量组成,累计R2X、R2Y和Q2值分别为0.351、0.988和0.975。另外,对相应的OPLS-DA模型进行了交叉验证和随机排列测试(200次)。图2d和2e分别为正、负离子模式下的置换检验图,随置换保留度下降,R2和Q2下降,回归线呈向上的趋势,这说明置换检验过关,模型不存在过拟合现象[25]。置换检验图中,正离子模式下R2回归线和Q2回归线的截距分别为0.1314和−1.0731;负离子模式下R2回归线和Q2回归线的截距分别为0.146和−0.8613。R2截距值小于0.3,Q2截距小于0.05也表示模型稳健可靠。PCA分析和OPLS-DA分析结果均表明西南区酿酒高粱常规品种与杂交品种间存在统计学差异。
2.2.2 常规高粱和杂交高粱的差异代谢物筛选
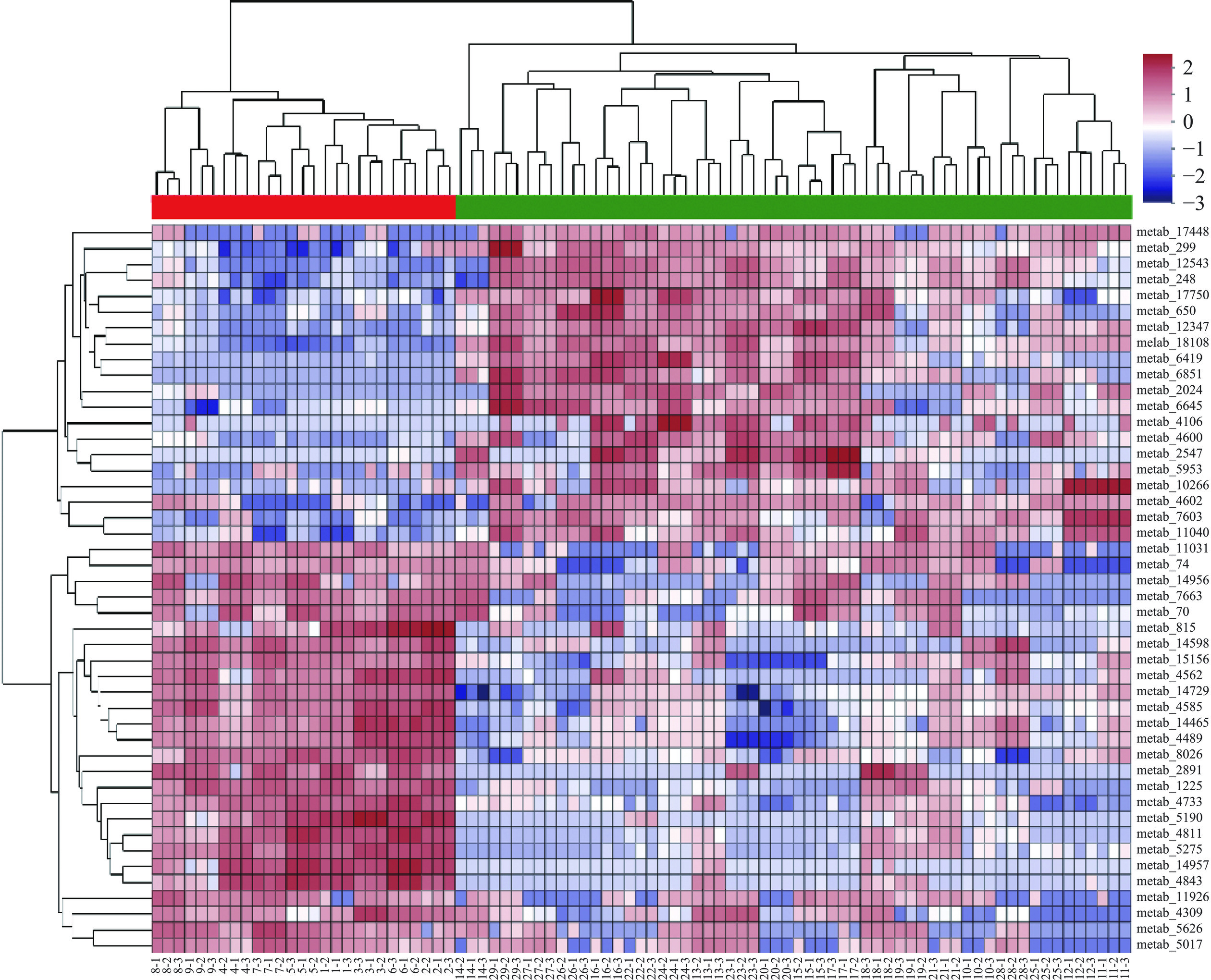
OPLS-DA模型的VIP值可以作为筛选不同品种类别酿酒高粱标志物的依据。按照VIP值>2,并且通过T检验后P<0.05,筛选出67个与品种相关的特征代谢物,其中21种物质由于HMDB数据库更新无法查询其结构信息,且在文献报道中几乎查询不到相关信息。因此初步筛选后剩下46种代谢物作为品种鉴别的标记物,如表2所示。以杂交高粱组的相对定量为对照,常规高梁组相对定量与杂交高粱组的相对定量的比值为差异表达倍数(fold change,FC)。FC大于1为上调,小于1为下调。常规高粱中有26种代谢物相比于杂交高粱是上调的,20种代谢物下调。以46种差异代谢物的相对定量值绘制聚类热图,如图3所示。由聚类分析结果可以看出,常规高粱和杂交高粱表现出明显的分组。上调的26种代谢物中有21种代谢物具有酚结构,其中2-阿魏酰-1,2'-二芥子酰龙胆二糖和3-O-p-香豆酰奎尼酸是以酯键形式结合的结合态酚类物质,N1,N5,N10-三咖啡酰亚精胺是含有咖啡酸结构的酚类衍生物。这些酚酸类衍生物可能在酿酒过程中经微生物转化或者酶解酯键而形成阿魏酸、咖啡酸和对香豆酸等[26]。阿魏酸是白酒中挥发性酚类物质4-甲/乙基愈创木酚的前体物质,4-甲/乙基愈创木酚是浓香型白酒中重要的风味和健康成分,是影响白酒烟熏、丁香风味及抗氧化、抗炎等健康特性的重要因素[27]。因此以含有更多结合态酚酸和酚酸类衍生物的常规高粱为酿酒原料,有助于提升白酒的风味层次感和抗氧化活性。
表 2 常规品种与其它杂交品种比较差异显著的代谢物信息Table 2. Metabolites with significant differences between conventional varieties and other hybrid varietiesMetab ID 加合离子模式 质荷比m/z 保留时间(min) 分子式 搜库
得分代谢物 VIP AUC RSD
(%)调节(C/NC) metab_5275 [2M+NH4]+ 846.2642 3.2786 C18H22O11 73.1 5-(3',4',5'-三羟基苯)-γ-戊内酯-O-甲基-4’-O-葡糖苷酸酯
5-(3',4',5'-trihydroxyphenyl)-gamma-valerolactone-O-methyl-4'-O-glucuronide3.06 1.000 4.61 上调 metab_1225 [M+H]+, [M+Na]+ 531.1101 4.8330 C23H24O13 33.9 丁香亭-3-葡萄糖苷
Syringetin 3-glucoside3.12 0.983 7.35 上调 metab_11031 [M+Na-2H]− 789.1881 4.1277 C34H40O20 86.3 6-[(2-{4-[(3-{[4-(羟基)-3-羟基-4-(羟甲基)氧基-2-基]氧基}-4,5-二羟基-6-(羟甲基)氧基-2-基)氧基]苯基}-4-氧基-3,4-二羟基- 2h -1-苯并吡喃-7-基)氧基]-3,4,5-三羟基氧基-2-羧酸
6-[(2-{4-[(3-{[4-(acetyloxy)-3-hydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl)oxy]phenyl}-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-7-yl)oxy]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid2.64 0.824 4.48 上调 metab_14957 [M-H]− 929.2708 4.9559 C44H50O22 89.9 2-阿魏酰-1,2'-二芥子酰龙胆二糖
2-Feruloyl-1,2'-disinapoylgentiobiose3.20 0.956 25.5 上调 metab_74 [M+H]+, [M+Na]+,
[M+NH4]+, [M+H-H2O]−453.1383 2.4804 C21H24O11 68.4 表儿茶素-3-O-β-D-异丙吡喃苷
Epicatechin-3-O-beta-D-allopyranoside2.34 0.794 1.72 上调 metab_4811 [M+2Na-H]+ 777.2195 4.4789 C39H40O14 67.6 6-[4-(6-羧基-5-{2,6-二羟基-4-[6-羟基-7-(3-甲基丁基-2-根-1-基)-1-苯并呋喃-2-基]苯基}-3-甲基环己基-3-根-1-基)-3-羟基苯氧]-3,4,5-三羟基氧烷-2-羧酸
6-[4-(6-carboxy-5-{2,6-dihydroxy-4-[6-hydroxy-7-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-1-benzofuran-2-yl]phenyl}-3-methylcyclohex-3-en-1-yl)-3-hydroxyphenoxy]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid3.30 0.980 5.8 上调 metab_7663 [M-H2O-H]−,
[M-H]−295.082 2.6799 C14H16O7 61.2 6-(3-乙烯基苯氧基)-3,4,5-三羟基氧烷-2-羧酸
6-(3-ethenylphenoxy)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid2.73 0.823 1.7 上调 metab_4489 [M+CH3OH+H]+ 251.0910 2.1581 C12H10O4 78.9 8-羟基-2-甲氧基-6-甲基-1,4-萘醌
8-Hydroxy-2-methoxy-6-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone2.37 0.962 3.75 上调 metab_5190 [M+Na]+ 525.1208 3.4633 C21H26O14 81.7 3,4,5-三羟基-6-{4-[(1E)-3-氧基-3-[(3,4,5,6-四羟基氧基-2-基)甲氧基]丙-1-根-1-基]苯氧基}氧基-2-羧酸
3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-{4-[(1E)-3-oxo-3-[(3,4,5,6-tetrahydroxyoxan-2-yl)methoxy]prop-1-en-1-yl]phenoxy}oxane-2-carboxylic acid2.80 0.972 4.13 上调 metab_5017 [M+H]+ 277.1066 3.9000 C15H16O5 53.5 壳二孢素
Ascochitin2.30 0.832 19.16 上调 metab_11926 [M-H]− 255.0296 5.8890 C14H8O5 73.9 红紫素
Purpurin2.03 0.838 10.83 上调 metab_4585 [M+H]+ 135.0440 5.3837 C8H6O2 66.3 反式6-辛烯-2,4-二炔酸
6E-Octene-2,4-diynoic acid2.33 0.983 1.86 上调 Metab_815 [M+H]+, [M+Na]+ 632.2586 5.1932 C34H37N3O9 60.8 N1,N5,N10-三咖啡酰亚精胺
N1,N5,N10-Tricaffeoyl spermidine2.02 0.839 14.99 上调 metab_8026 [M+FA-H]−,
[2M-H]−915.2552 4.6144 C23H22O10 69.2 6''-O-乙酰大豆苷
6''-O-Acetyldaidzin2.20 0.986 8.27 上调 metab_4843 [2M+H]+ 677.2060 4.4178 C16H18O8 93.3 3-O-p-香豆酰奎尼酸
3-O-p-Coumaroylquinic acid2.76 0.973 13.04 上调 metab_2891 [M+H]+ 291.1221 4.4111 C16H18O5 60.2 5-O-甲维阿斯米醇
5-O-Methylvisamminol2.76 0.887 19.65 上调 metab_4309 [M+K]+ 523.1383 6.0006 C26H28O9 60.8 6-{[2,2-二甲基-6-(3-氧基-3-苯丙基)- 2H -色烯-5-基]氧}-3,4,5-三羟基氧烷-2-羧酸
6-{[2,2-dimethyl-6-(3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)-2H-chromen-5-yl]oxy}-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid2.05 0.814 2.36 上调 metab_70 [M+H]+, [M+Na]+, [M+NH4]+, [M+K]+ 323.0755 2.7867 C15H14O8 52.5 没食子酸儿茶素-4β-醇
Gallocatechin-4beta-ol2.02 0.782 1.74 上调 metab_14598 [M+FA-H]− 827.1821 5.5634 C34H38O21 65.5 6-{4-[7-({6-[(乙酰氧基)甲基]-3-{[3,4-二羟基-4-(羟甲基)-2-四氢呋喃基]氧}-4,5-二羟基-2-基}氧)-5-羟基-4-氧- 4H -色烯-2-基]苯氧}-3,4,5-三羟基氧烷-2-羧酸
6-{4-[7-({6-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-3-{[3,4-dihydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxyoxan-2-yl}oxy)-5-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-2-yl]phenoxy}-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid2.44 0.938 7.73 上调 metab_5626 [M+H]+ 275.0908 2.5486 C15H14O5 50.4 科里内酯醛苯甲酸酯
Corey Lactone Aldehyde Benzoate2.62 0.846 6.67 上调 metab_14956 [M+FA-H]− 323.0769 4.963 C14H14O6 61.5 3,9-二羟基-2-(2-羟丙基-2-基)- 2H,3H, 7H -呋喃[3,2-g]色烯-7-酮
3,9-dihydroxy-2-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2H,3H,7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one2.10 0.730 1.64 上调 metab_15156 [M+Cl]− 411.0718 4.6899 C15H20O11 65.2 呋喃酮4-(6-丙二酰糖苷)
Furaneol 4-(6-malonylglucoside)2.03 0.972 3.61 上调 metab_4562 [M+H-H2O]+ 397.0911 5.4716 C21H18O9 91.9 3,4,5-三羟基-6-[(4-氧-2-苯基- 4H -色烯-3-基)氧]氧烷-2-羧酸
3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[(4-oxo-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-3-yl)oxy]oxane-2-carboxylic acid2.14 0.919 20.93 上调 metab_14465 [M+Na-2H]− 428.1101 5.7275 C15H25N3O8S 52 γ-l-谷氨酰胺-γ-l-谷氨酰胺-l-蛋氨酸
Gamma-L-Glutamyl-gamma-L-glutamyl-L-methionine2.06 0.962 11.17 上调 metab_14729 [M+Cl]− 531.01 5.3731 C21H18Cl2N2O8 79 劳拉西泮葡糖苷酸
Lorazepam glucuronide2.05 0.984 8.25 上调 metab_4733 [M+H]+ 339.1068 4.7306 C16H18O8 79.7 α-氢化胡桃醌4-O-b-D-葡萄糖
Alpha-Hydrojuglone 4-O-b-D-glucoside2.61 0.989 6.74 上调 metab_17448 [M+K-2H]− 451.1201 1.9155 C23H26O7 82.8 藤黄酮C
Garcinone C2.94 0.891 23.03 下调 metab_6851 [M+H]+ 89.1077 0.5021 C4H12N2 56.6 腐胺
Putrescine2.66 0.942 8.66 下调 metab_4106 [M+H]+ 452.2765 6.2425 C21H42NO7P 93.3 甘油磷酸乙醇胺LysoPE(16:1(9Z)/0:0) 2.38 0.738 21.42 下调 metab_10266 [M+FA-H]− 581.1510 2.7497 C25H28O13 86.6 牛痘苷
Vaccinoside2.36 0.813 15.05 下调 metab_2024 [M+H-2H2O]+ 291.01925 0.9285 C9H12FN2O8P 55.6 5-氟脱氧尿苷一磷酸
5-Fluorodeoxyuridine monophosphate2.20 0.870 12.89 下调 metab_4602 [M+H]+ 515.1792 5.3019 C29H26N2O7 54.1 TyrMe-Nap-OH 2.63 0.829 15.63 下调 metab_6419 [M+H]+ 131.1179 0.9217 C6H14N2O 52.5 N-乙酰腐胺
N-Acetylputrescine2.40 0.914 3.14 下调 metab_18108 [M-H]− 209.0297 0.6205 C6H10O8 68.5 D-葡萄糖酸 D-Glucarate 2.35 0.993 3.96 下调 metab_2547 [M+ACN+Na]+ 309.1804 2.8617 C12H23NO4 54.1 2-甲基丁基肉碱
2-Methylbutyroylcarnitine2.04 0.766 4.45 下调 metab_12347 [M+FA-H]− 384.2753 6.3301 C20H37NO3 67.5 油酰甘氨酸
Oleoyl glycine2.31 0.927 6.62 下调 metab_4600 [M+H]+ 265.1431 5.3224 C15H20O4 72.6 倍半萜内酯326
Sequiterpene Lactone 3262.13 0.888 14.53 下调 metab_7603 [M-H2O-H]−, [M-H]− 479.1191 2.3369 C22H24O12 86.9 4'-O-甲基-(-)-表儿茶素3'-O-葡糖苷酸
4'-O-Methyl-(-)-epicatechin 3'-O-glucuronide2.69 0.898 2.22 下调 metab_17750 [M-H]− 174.0402 1.2001 C6H9NO5 54.3 N-乙酰天冬氨酸
N-acetylaspartate2.17 0.904 2.51 下调 metab_299 [M+H-H2O]+, [M+H]+, [M+H-2H2O]+ 293.2108 5.4579 C18H30O4 58.7 (9Z,11R,12S,13S,15Z)-12,13-环氧-11-羟基-9,15-十八碳二烯酸
(9Z,11R,12S,13S,15Z)-12,13-Epoxy-11-hydroxy-9,15-octadecadienoic acid2.20 0.931 12.97 下调 metab_11040 [M-H2O-H]− 475.1244 4.1477 C23H26O12 67.4 4'-O-甲基-(-)-表儿茶素-3'-O-β-葡糖苷酸
4'-O-methyl-(-)-epicatechin-3'-O-beta-glucuronide2.12 0.956 4.85 下调 metab_650 [M+2Na-H]+, [2M+ACN+Na]+ 295.1285 3.1010 C15H22O3 56.6 1-羟基乙酰丙酮
1-Hydroxyacorenone2.08 0.862 3.51
下调metab_5953 [M+ACN+H]+ 266.1018 2.0301 C11H12O5 52.2 5-[(2,4,5-三羟基苯基)甲基]四氢呋喃-
2-酮
5-[(2,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)methyl]oxolan-2-one2.06 0.800 11.32 下调 metab_6645 [M+H]+ 147.0763 0.6088 C5H10N2O3 92.4 L-谷氨酰胺
L-Glutamine2.05 0.905 1.73 下调 metab_12543 [M+Na-2H]− 551.2597 7.0145 C30H42O8 69.5 卡维汀A
Cavipetin A2.38 0.947 4.51 下调 metab_248 [M+Na]+, [M+2Na-H]+, [M+H]+ 507.2091 7.02 C22H45O9P 75.4 磷脂酰甘油PG(16:0/0:0)[U] 2.43 0.928 5.3 下调 注:Metab ID,代谢物编号;搜库得分,通过质谱信息搜索美吉生物公司标品自建库、Metlin、LipidBlast、HMDB数据库的匹配得分;AUC,代谢物ROC分析曲线下面积;RSD,质控样本中代谢物峰面积的相对标准偏差。 丁香亭-3-葡萄糖苷、表儿茶素-3-O-β-D-异丙吡喃苷、metab_11031(甘草素衍生物)、metab_14958(芹菜素衍生物)、metab_4562、没食子酸儿茶素-4β-醇和6''-O-乙酰大豆苷等7种黄酮类衍生物也在西南地区常规酿酒高粱中含量更高。研究表明,这些高粱黄酮类物质常具有抗氧化、抗炎症等生物活性[28]。目前对于白酒中黄酮类物质的研究较少,但是参考葡萄酒相关研究,高粱中的黄酮类物质经过酿造过程一部分进入到基酒中,可能对白酒的滋味与健康功效作出贡献。如表2所示常规高粱中γ-l-谷氨酰胺-γ-l-谷氨酰胺-l-蛋氨酸相对含量高于杂交高粱。在酱香型白酒含硫挥发性化合物的分析中可检测到烯丙硫醇、正丁硫醇、3-甲基-2-丁硫醇和甲硫醇等硫醇类化合物,其形成原因可能是酵母对酿酒原料中的含硫蛋白质,如蛋氨酸的代谢产生[29]。所以酿酒高粱品种对白酒酚类及硫醇类化合物的含量有一定影响。西南地区主产浓香型白酒和酱香型白酒的独特风味可能与常规高粱中富含的酚类物质和上调的氨基酸存在一定的联系。其它差异代谢物对白酒酿造的影响还需在后续结合酿造试验中白酒的风味和功效成分进行关联分析。
2.2.3 基于主要差异代谢物的品种鉴别模型构建
将选定的46个差异代谢物作为品种鉴别标记物建立PCA模型,模型累计R2X为0.763,Q2为0.62。如图4a所示常规高粱和其它杂交高粱分离良好,常规高粱和杂交高粱分别聚集在PC1轴的左右两侧,2.1中所述根据理化性质无法正确分类的瑞杂1号和内杂5号也被正确分配到相应的簇中,基于46个差异代谢物的PCA模型具有较好的分类能力,这也说明潜在标记物具有可靠性和通用性。此外,基于46个潜在标记物建立的OPLS-DA模型,其包含1个预测分量和4个正交分量。累计R2X、R2Y和Q2分别为0.725、0.971和0.95。由表3可知OPLS-DA模型内部预测中没有高粱样品被错误分类。
表 3 OPLS-DA模型判断结果Table 3. OPLS-DA model judgment results品种 样本数量
(个)判定正确数
(个)判定错误数
(个)正确率
(%)杂交品种 60 60 0 100 常规品种 27 27 0 100 合计 87 87 0 100 2.2.4 主要差异代谢物的ROC分析和丰度比较
尽管基于46个主要差异代谢物的PCA和OPLS-DA模型对常规高粱和其它高粱的分类效果是可行的,仍有必要进一步探究不同类别高粱的特定标记物。受试者工作特征曲线是一种用于评估生物标志物预测性能的实用图形工具,可表示生物标志物区分两组的能力。这些标记物在每个ROC模型中有相应的曲线下面积(area under curve,AUC),是预测精度的数值解释,其值在0~1之间波动,与精度呈正相关。一般AUC值为0.5~0.7时,表示诊断准确性较低;AUC值为0.7~0.9时,表示诊断正确性中等;而面积AUC值大于0.9时,表示诊断准确性较高,AUC等于0.5时,说明诊断方法完全不起作用[30]。对表2中列出的46种差异代谢物进行ROC分析,其中有25个代谢物的AUC值大于0.9。另外,一个理想的标记物应当具备良好的重现性,因此进一步要求标记物在质控样品中的RSD小于10%[8],因此满足条件的差异代谢物剩下20个。它们的丰度表达比较如下图5所示。常规高粱组的丁香亭-3-葡萄糖苷相对丰度平均值是杂交高粱组的1.37倍。Zhou等[31]在研究不同颜色的甜高粱品种中类黄酮代谢组差异时,发现红色籽粒高粱中丁香亭-7-O-己糖苷显著高于白色籽粒品种,由此可推测本研究中丁香亭糖苷类物质相对含量在常规高粱组更高可能与常规高粱籽粒的颜色有关。丁香亭-3-葡萄糖苷也常在酿酒葡萄及葡萄酒中检出,研究表明其苷元−紫丁香素,及其他衍生物具有抗氧化、抗炎、抑菌、抑癌等药理作用[32]。在本研究中,常规高粱品种的6''-O-乙酰大豆苷的表达丰度高于杂交高粱。6''-O-乙酰大豆苷是一种异黄酮-糖苷,通常在大豆和豆奶中含量较高[33],但Xiong等[34]在研究不同基因型高粱的酚类物质时也发现了6''-O-乙酰大豆苷。D-葡萄糖酸在常规高粱中的丰度平均值为杂交高粱组的0.80倍,而且常规高粱的组内平均值标准误差(standard error of the mean,SEM)为5.95%(n=27),杂交高粱的SEM为6.02%(n=60),这说明D-葡萄糖酸的含量主要受到遗传背景的影响,没有因为高粱的生长地点不同而产生差异。它在杂交高粱中丰度更高,因此可以作为杂交高粱存在的标记。Pavli等[35]在高粱的叶片和根中均检测到D-葡萄糖酸,而且受干旱胁迫的高粱植株叶片中D-葡萄糖酸含量显著高于对照。此外杂交高粱中腐胺、N-乙酰腐胺和L-谷氨酰胺的相对含量分别是常规高粱的1.51、1.47和1.19倍。Paiva等[36]研究发现不含单宁的高粱比含单宁的高粱更大概率检测到腐胺。这与本研究结果相似,杂交高粱的单宁含量低于常规高粱,其腐胺相对含量更高。腐胺和L-谷氨酰胺在植物抵抗干旱、病害等外界胁迫时发挥重要作用[36−37],因此杂交高粱抗性更强可能与较高含量的腐胺和谷氨酰胺有关。丁香亭-3-葡萄糖苷等6种标记物可以购买相应标品,并且文献已报道定性定量方法[38−41],后续可通过液相色谱或液质联用进行定量研究,应用于酿酒高粱常规品种质量监控与防伪。
3. 结论
本研究发现西南地区常规品种的支链淀粉和单宁含量偏高,直链淀粉含量和千粒重偏低,基于理化性质可实现部分样品的鉴别。使用非靶向代谢组学结合OPLS-DA分析筛选出46种主要差异代谢物,其中26种差异代谢物在西南地区常规品种中表达丰度更高且大多数为酚类物质,说明西南地区常规品种的又一特性是含有更丰富的酚类物质。采用筛选出的46个差异代谢物重新构建的高粱品种判别模型,对高粱品种类别判别正确率达到100%,满足高粱品种判别的需要。另外,基于受试者工作特征曲线分析和质控样本的相对标准偏差进一步筛选出20个诊断准确性较高且重现性较好的差异代谢物。其中丁香亭-3-葡萄糖苷和6''-O-乙酰大豆苷在常规高粱品种中具有更高的表达丰度,D-葡萄糖酸、腐胺、N-乙酰腐胺和L-谷氨酰胺在杂交高粱中含量更高。本研究通过基本理化和非靶向代谢组学实现了西南地区酿酒高粱常规品种的初步鉴别和特性分析,筛选出品种鉴别的特征成分,可为后续开发更为简捷的鉴别方法提供基础。
-
表 1 高粱样品信息
Table 1 Information of the sorghum samples tested in this study
编号 品种名称 类别 编号 品种名称 类别 1 红缨子 常规 16 汉青1号 杂交 2 青壳洋 17 红糯13号 3 国窖红1号 18 瑞杂1号 4 宜糯红4号 19 齐杂7号 5 郎糯红19号 20 吉杂210 6 水儿红 21 红茅6号 7 青壳洋 22 晋杂22号 8 国窖红1号 23 晋杂23 9 泸州红1号 24 冀酿4号 10 兴颗3
杂交25 国酿红235 11 金糯粱6号 26 晋杂22号 12 机糯粱1号 27 凤杂18号 13 齐杂104 28 凤杂4号 14 内杂5号 29 东梁80 15 齐糯115 表 2 常规品种与其它杂交品种比较差异显著的代谢物信息
Table 2 Metabolites with significant differences between conventional varieties and other hybrid varieties
Metab ID 加合离子模式 质荷比m/z 保留时间(min) 分子式 搜库
得分代谢物 VIP AUC RSD
(%)调节(C/NC) metab_5275 [2M+NH4]+ 846.2642 3.2786 C18H22O11 73.1 5-(3',4',5'-三羟基苯)-γ-戊内酯-O-甲基-4’-O-葡糖苷酸酯
5-(3',4',5'-trihydroxyphenyl)-gamma-valerolactone-O-methyl-4'-O-glucuronide3.06 1.000 4.61 上调 metab_1225 [M+H]+, [M+Na]+ 531.1101 4.8330 C23H24O13 33.9 丁香亭-3-葡萄糖苷
Syringetin 3-glucoside3.12 0.983 7.35 上调 metab_11031 [M+Na-2H]− 789.1881 4.1277 C34H40O20 86.3 6-[(2-{4-[(3-{[4-(羟基)-3-羟基-4-(羟甲基)氧基-2-基]氧基}-4,5-二羟基-6-(羟甲基)氧基-2-基)氧基]苯基}-4-氧基-3,4-二羟基- 2h -1-苯并吡喃-7-基)氧基]-3,4,5-三羟基氧基-2-羧酸
6-[(2-{4-[(3-{[4-(acetyloxy)-3-hydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl)oxy]phenyl}-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-7-yl)oxy]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid2.64 0.824 4.48 上调 metab_14957 [M-H]− 929.2708 4.9559 C44H50O22 89.9 2-阿魏酰-1,2'-二芥子酰龙胆二糖
2-Feruloyl-1,2'-disinapoylgentiobiose3.20 0.956 25.5 上调 metab_74 [M+H]+, [M+Na]+,
[M+NH4]+, [M+H-H2O]−453.1383 2.4804 C21H24O11 68.4 表儿茶素-3-O-β-D-异丙吡喃苷
Epicatechin-3-O-beta-D-allopyranoside2.34 0.794 1.72 上调 metab_4811 [M+2Na-H]+ 777.2195 4.4789 C39H40O14 67.6 6-[4-(6-羧基-5-{2,6-二羟基-4-[6-羟基-7-(3-甲基丁基-2-根-1-基)-1-苯并呋喃-2-基]苯基}-3-甲基环己基-3-根-1-基)-3-羟基苯氧]-3,4,5-三羟基氧烷-2-羧酸
6-[4-(6-carboxy-5-{2,6-dihydroxy-4-[6-hydroxy-7-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-1-benzofuran-2-yl]phenyl}-3-methylcyclohex-3-en-1-yl)-3-hydroxyphenoxy]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid3.30 0.980 5.8 上调 metab_7663 [M-H2O-H]−,
[M-H]−295.082 2.6799 C14H16O7 61.2 6-(3-乙烯基苯氧基)-3,4,5-三羟基氧烷-2-羧酸
6-(3-ethenylphenoxy)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid2.73 0.823 1.7 上调 metab_4489 [M+CH3OH+H]+ 251.0910 2.1581 C12H10O4 78.9 8-羟基-2-甲氧基-6-甲基-1,4-萘醌
8-Hydroxy-2-methoxy-6-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone2.37 0.962 3.75 上调 metab_5190 [M+Na]+ 525.1208 3.4633 C21H26O14 81.7 3,4,5-三羟基-6-{4-[(1E)-3-氧基-3-[(3,4,5,6-四羟基氧基-2-基)甲氧基]丙-1-根-1-基]苯氧基}氧基-2-羧酸
3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-{4-[(1E)-3-oxo-3-[(3,4,5,6-tetrahydroxyoxan-2-yl)methoxy]prop-1-en-1-yl]phenoxy}oxane-2-carboxylic acid2.80 0.972 4.13 上调 metab_5017 [M+H]+ 277.1066 3.9000 C15H16O5 53.5 壳二孢素
Ascochitin2.30 0.832 19.16 上调 metab_11926 [M-H]− 255.0296 5.8890 C14H8O5 73.9 红紫素
Purpurin2.03 0.838 10.83 上调 metab_4585 [M+H]+ 135.0440 5.3837 C8H6O2 66.3 反式6-辛烯-2,4-二炔酸
6E-Octene-2,4-diynoic acid2.33 0.983 1.86 上调 Metab_815 [M+H]+, [M+Na]+ 632.2586 5.1932 C34H37N3O9 60.8 N1,N5,N10-三咖啡酰亚精胺
N1,N5,N10-Tricaffeoyl spermidine2.02 0.839 14.99 上调 metab_8026 [M+FA-H]−,
[2M-H]−915.2552 4.6144 C23H22O10 69.2 6''-O-乙酰大豆苷
6''-O-Acetyldaidzin2.20 0.986 8.27 上调 metab_4843 [2M+H]+ 677.2060 4.4178 C16H18O8 93.3 3-O-p-香豆酰奎尼酸
3-O-p-Coumaroylquinic acid2.76 0.973 13.04 上调 metab_2891 [M+H]+ 291.1221 4.4111 C16H18O5 60.2 5-O-甲维阿斯米醇
5-O-Methylvisamminol2.76 0.887 19.65 上调 metab_4309 [M+K]+ 523.1383 6.0006 C26H28O9 60.8 6-{[2,2-二甲基-6-(3-氧基-3-苯丙基)- 2H -色烯-5-基]氧}-3,4,5-三羟基氧烷-2-羧酸
6-{[2,2-dimethyl-6-(3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)-2H-chromen-5-yl]oxy}-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid2.05 0.814 2.36 上调 metab_70 [M+H]+, [M+Na]+, [M+NH4]+, [M+K]+ 323.0755 2.7867 C15H14O8 52.5 没食子酸儿茶素-4β-醇
Gallocatechin-4beta-ol2.02 0.782 1.74 上调 metab_14598 [M+FA-H]− 827.1821 5.5634 C34H38O21 65.5 6-{4-[7-({6-[(乙酰氧基)甲基]-3-{[3,4-二羟基-4-(羟甲基)-2-四氢呋喃基]氧}-4,5-二羟基-2-基}氧)-5-羟基-4-氧- 4H -色烯-2-基]苯氧}-3,4,5-三羟基氧烷-2-羧酸
6-{4-[7-({6-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-3-{[3,4-dihydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxyoxan-2-yl}oxy)-5-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-2-yl]phenoxy}-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid2.44 0.938 7.73 上调 metab_5626 [M+H]+ 275.0908 2.5486 C15H14O5 50.4 科里内酯醛苯甲酸酯
Corey Lactone Aldehyde Benzoate2.62 0.846 6.67 上调 metab_14956 [M+FA-H]− 323.0769 4.963 C14H14O6 61.5 3,9-二羟基-2-(2-羟丙基-2-基)- 2H,3H, 7H -呋喃[3,2-g]色烯-7-酮
3,9-dihydroxy-2-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2H,3H,7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one2.10 0.730 1.64 上调 metab_15156 [M+Cl]− 411.0718 4.6899 C15H20O11 65.2 呋喃酮4-(6-丙二酰糖苷)
Furaneol 4-(6-malonylglucoside)2.03 0.972 3.61 上调 metab_4562 [M+H-H2O]+ 397.0911 5.4716 C21H18O9 91.9 3,4,5-三羟基-6-[(4-氧-2-苯基- 4H -色烯-3-基)氧]氧烷-2-羧酸
3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[(4-oxo-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-3-yl)oxy]oxane-2-carboxylic acid2.14 0.919 20.93 上调 metab_14465 [M+Na-2H]− 428.1101 5.7275 C15H25N3O8S 52 γ-l-谷氨酰胺-γ-l-谷氨酰胺-l-蛋氨酸
Gamma-L-Glutamyl-gamma-L-glutamyl-L-methionine2.06 0.962 11.17 上调 metab_14729 [M+Cl]− 531.01 5.3731 C21H18Cl2N2O8 79 劳拉西泮葡糖苷酸
Lorazepam glucuronide2.05 0.984 8.25 上调 metab_4733 [M+H]+ 339.1068 4.7306 C16H18O8 79.7 α-氢化胡桃醌4-O-b-D-葡萄糖
Alpha-Hydrojuglone 4-O-b-D-glucoside2.61 0.989 6.74 上调 metab_17448 [M+K-2H]− 451.1201 1.9155 C23H26O7 82.8 藤黄酮C
Garcinone C2.94 0.891 23.03 下调 metab_6851 [M+H]+ 89.1077 0.5021 C4H12N2 56.6 腐胺
Putrescine2.66 0.942 8.66 下调 metab_4106 [M+H]+ 452.2765 6.2425 C21H42NO7P 93.3 甘油磷酸乙醇胺LysoPE(16:1(9Z)/0:0) 2.38 0.738 21.42 下调 metab_10266 [M+FA-H]− 581.1510 2.7497 C25H28O13 86.6 牛痘苷
Vaccinoside2.36 0.813 15.05 下调 metab_2024 [M+H-2H2O]+ 291.01925 0.9285 C9H12FN2O8P 55.6 5-氟脱氧尿苷一磷酸
5-Fluorodeoxyuridine monophosphate2.20 0.870 12.89 下调 metab_4602 [M+H]+ 515.1792 5.3019 C29H26N2O7 54.1 TyrMe-Nap-OH 2.63 0.829 15.63 下调 metab_6419 [M+H]+ 131.1179 0.9217 C6H14N2O 52.5 N-乙酰腐胺
N-Acetylputrescine2.40 0.914 3.14 下调 metab_18108 [M-H]− 209.0297 0.6205 C6H10O8 68.5 D-葡萄糖酸 D-Glucarate 2.35 0.993 3.96 下调 metab_2547 [M+ACN+Na]+ 309.1804 2.8617 C12H23NO4 54.1 2-甲基丁基肉碱
2-Methylbutyroylcarnitine2.04 0.766 4.45 下调 metab_12347 [M+FA-H]− 384.2753 6.3301 C20H37NO3 67.5 油酰甘氨酸
Oleoyl glycine2.31 0.927 6.62 下调 metab_4600 [M+H]+ 265.1431 5.3224 C15H20O4 72.6 倍半萜内酯326
Sequiterpene Lactone 3262.13 0.888 14.53 下调 metab_7603 [M-H2O-H]−, [M-H]− 479.1191 2.3369 C22H24O12 86.9 4'-O-甲基-(-)-表儿茶素3'-O-葡糖苷酸
4'-O-Methyl-(-)-epicatechin 3'-O-glucuronide2.69 0.898 2.22 下调 metab_17750 [M-H]− 174.0402 1.2001 C6H9NO5 54.3 N-乙酰天冬氨酸
N-acetylaspartate2.17 0.904 2.51 下调 metab_299 [M+H-H2O]+, [M+H]+, [M+H-2H2O]+ 293.2108 5.4579 C18H30O4 58.7 (9Z,11R,12S,13S,15Z)-12,13-环氧-11-羟基-9,15-十八碳二烯酸
(9Z,11R,12S,13S,15Z)-12,13-Epoxy-11-hydroxy-9,15-octadecadienoic acid2.20 0.931 12.97 下调 metab_11040 [M-H2O-H]− 475.1244 4.1477 C23H26O12 67.4 4'-O-甲基-(-)-表儿茶素-3'-O-β-葡糖苷酸
4'-O-methyl-(-)-epicatechin-3'-O-beta-glucuronide2.12 0.956 4.85 下调 metab_650 [M+2Na-H]+, [2M+ACN+Na]+ 295.1285 3.1010 C15H22O3 56.6 1-羟基乙酰丙酮
1-Hydroxyacorenone2.08 0.862 3.51
下调metab_5953 [M+ACN+H]+ 266.1018 2.0301 C11H12O5 52.2 5-[(2,4,5-三羟基苯基)甲基]四氢呋喃-
2-酮
5-[(2,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)methyl]oxolan-2-one2.06 0.800 11.32 下调 metab_6645 [M+H]+ 147.0763 0.6088 C5H10N2O3 92.4 L-谷氨酰胺
L-Glutamine2.05 0.905 1.73 下调 metab_12543 [M+Na-2H]− 551.2597 7.0145 C30H42O8 69.5 卡维汀A
Cavipetin A2.38 0.947 4.51 下调 metab_248 [M+Na]+, [M+2Na-H]+, [M+H]+ 507.2091 7.02 C22H45O9P 75.4 磷脂酰甘油PG(16:0/0:0)[U] 2.43 0.928 5.3 下调 注:Metab ID,代谢物编号;搜库得分,通过质谱信息搜索美吉生物公司标品自建库、Metlin、LipidBlast、HMDB数据库的匹配得分;AUC,代谢物ROC分析曲线下面积;RSD,质控样本中代谢物峰面积的相对标准偏差。 表 3 OPLS-DA模型判断结果
Table 3 OPLS-DA model judgment results
品种 样本数量
(个)判定正确数
(个)判定错误数
(个)正确率
(%)杂交品种 60 60 0 100 常规品种 27 27 0 100 合计 87 87 0 100 -
[1] 孙婷. 高粱品种的高光谱分类及多品种混合识别研究[D]. 自贡:四川轻化工大学, 2021. [[SUN T. Research on hyperspectral classification of sorghum varieties and multiple varieties mixed recognition[D]. Zigong:Sichuan University of Science & Engineering, 2021.] [SUN T. Research on hyperspectral classification of sorghum varieties and multiple varieties mixed recognition[D]. Zigong: Sichuan University of Science & Engineering, 2021.
[2] 郭喜祥. 高粱高产栽培技术[J]. 现代农业,2019(3):2. [GUO X X. High yield cultivation technology of sorghum[J]. Modern Agriculture,2019(3):2.] GUO X X. High yield cultivation technology of sorghum[J]. Modern Agriculture, 2019(3): 2.
[3] 戈刚. 什么是杂交高粱[J]. 中国农垦,1966(3):45. [GE G. What is hybrid sorghum[J]. China State Farm,1966(3):45.] GE G. What is hybrid sorghum[J]. China State Farm, 1966(3): 45.
[4] 闫松显, 吕云怀, 王莉, 等. 西南区酿酒高粱的种质形成与发展[J]. 中国酿造,2017,36(5):17−21. [YAN S X, LÜ Y H, WANG L, et al. Germplasm formation and development of Baijiu-making sorghum in the southwest of China[J]. China Brewing,2017,36(5):17−21.] YAN S X, LÜ Y H, WANG L, et al. Germplasm formation and development of Baijiu-making sorghum in the southwest of China[J]. China Brewing, 2017, 36(5): 17−21.
[5] 袁蕊, 敖中华, 刘小刚, 等. 南北方几种高粱酿酒品质分析[J]. 酿酒科技,2011,12:33−36. [YUAN R, AO Z H, LIU X G, et al. Brewing quality analysis of some kinds of sorghum in north and in south China[J]. Liquor-Making Science & Technology,2011,12:33−36.] YUAN R, AO Z H, LIU X G, et al. Brewing quality analysis of some kinds of sorghum in north and in south China[J]. Liquor-Making Science & Technology, 2011, 12: 33−36.
[6] 卫永太, 张镔, 张桂香. 中国高梁品质性状的区域性差异[J]. 天津农业科学,2016,22(11):138−140. [WEI Y T, ZHANG B, ZHANG G X. Regional differences analysis on quality traits of Chinese sorghum[J]. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences,2016,22(11):138−140.] WEI Y T, ZHANG B, ZHANG G X. Regional differences analysis on quality traits of Chinese sorghum[J]. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 22(11): 138−140.
[7] 闫松显, 袁河, 雷元春, 等. 酿酒高粱籽粒微观形态分析及其果皮厚度和单宁含量的相关性[J]. 中国酿造,2018,37(3):67−71. [YAN S X, YUAN H, LEI Y C, et al. Micro-morphology analysis of liquor-making sorghums grain and the correlation of pericarp thickness and tannin content[J]. China Brewing,2018,37(3):67−71.] YAN S X, YUAN H, LEI Y C, et al. Micro-morphology analysis of liquor-making sorghums grain and the correlation of pericarp thickness and tannin content[J]. China Brewing, 2018, 37(3): 67−71.
[8] RIGHETTI L, RUBERT J, GALAVERNA G, et al. A novel approach based on untargeted lipidomics reveals differences in the lipid pattern among durum and common wheat[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,240(Feb.1):775−783.
[9] 徐春晖, 王远兴. 基于UPLC-QTOF-MS结合非靶向代谢组学鉴别3种江西名茶[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(2):316−323. [[XU C H, WANG Y X. Non-targeted metabolomics based on ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry for discrimination of three Jiangxi famous teas[J]. Food Science,2022,43(2):316−323.] [XU C H, WANG Y X. Non-targeted metabolomics based on ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry for discrimination of three Jiangxi famous teas[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(2): 316−323.
[10] 倪德让. 一种基于挥发性物质组成特征的高粱品种鉴别方法:中国, 202210686274[P]. 2022-09-13. [NI D R. A method for sorghum variety identification based on volatile substance composition characteristics:China, 202210686274[P]. 2022-09-13.] NI D R. A method for sorghum variety identification based on volatile substance composition characteristics: China, 202210686274[P]. 2022-09-13.
[11] ZHOU Y X, WANG Z G, LI Y, et al. Metabolite profiling of sorghum seeds of different colors from different sweet sorghum cultivars using a widely targeted metabolomics approach[J]. International Journal of Genomics,2020,2020:6247429.
[12] RAMALINGAM A P, MOHANAVEL W, PREMNATH A, et al. Large-scale non-targeted metabolomics reveals antioxidant, nutraceutical and therapeutic potentials of sorghum[J]. Antioxidants,2021,10(10):1511.
[13] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.9-2016 食品中淀粉的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.9-2016 Determination of starch in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.9-2016 Determination of starch in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[14] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局 GB 5009.6-2016 食品中脂肪的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.6-2016 Determination of fat in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.6-2016 Determination of fat in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[15] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局 GB 5009.5-2016 食品中蛋白质的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.6-2016 Determination of protein in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.6-2016 Determination of protein in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[16] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 15686-2008高粱 单宁含量的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2008. [General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 15686-2008 Determination of tannin content in sorghum[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2008.] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 15686-2008 Determination of tannin content in sorghum[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008.
[17] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 15683-2008 大米 直链淀粉含量的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2008. [General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 15683-2008 Determination of amylose content in rice[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2008.] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 15683-2008 Determination of amylose content in rice[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008.
[18] 徐晓, 任根增, 赵欣蕊, 等. 中国高粱地方品种和育成品种穗部表型性状精准鉴定及综合评价[J]. 中国农业科学,2022,55(11):2092−2108. [XU X, REN G Z, ZHAO X R, et al. Accurate identification and comprehensive evaluation of panicle phenotypic traits of landraces and cultivars of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2022,55(11):2092−2108.] XU X, REN G Z, ZHAO X R, et al. Accurate identification and comprehensive evaluation of panicle phenotypic traits of landraces and cultivars of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(11): 2092−2108.
[19] 王红梅, 李哲, 李令, 等. 川南白酒产区主要酿酒高粱理化性质与代谢组学分析[J]. 酿酒科技,2023,7:44−56. [WANG H M, LI Z, LI L, et al. Physicochemical properties and metabolomics of liquor-making sorghum from southern Sichuan[J]. Liquor-Making Science & Technology,2023,7:44−56.] WANG H M, LI Z, LI L, et al. Physicochemical properties and metabolomics of liquor-making sorghum from southern Sichuan[J]. Liquor-Making Science & Technology, 2023, 7: 44−56.
[20] ZHOU L L, WANG D F, ZHOU H L. Metabolic profiling of two medicinal piper species[J]. South African Journal of Botany,2021,139:281−289. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2021.03.007
[21] 韩静雯, 李国辉, 钟其顶, 等. 基于超高效液相色谱-四极杆/飞行时间质谱鉴别红葡萄酒的品种和产地[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(19):250−256. [HAN J W, LI G H, ZHONG Q D, et al. Identification of red wine varieties and origins based on the ultra-high performance liquid chromalography-quadrupole/time of flight mass a spectrometry[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(19):250−256.] HAN J W, LI G H, ZHONG Q D, et al. Identification of red wine varieties and origins based on the ultra-high performance liquid chromalography-quadrupole/time of flight mass a spectrometry[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 48(19): 250−256.
[22] LI Y H, LIANG L, XU C H, et al. UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-based untargeted metabolomics for discrimination of navel oranges from different geographical origins of China[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,137:110382. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110382
[23] RIGHETTI L, RUBERT J, GALAVERNA G, et al. A novel approach based on the untargeted lipidomics reveals differences in the lipid pattern among durum and common wheat[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,240:775−783. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.08.020
[24] 徐冰冰, 张九凯, 赵贵明, 等. 基于非靶标代谢组学的沙棘油真实性鉴别技术[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(18):246−253. [XU B B, ZHANG J K, ZHAO G M, et al. Authentication of sea buckthorn oil based on non-targeted metabolomic[J]. Food Science,2021,42(18):246−253.] XU B B, ZHANG J K, ZHAO G M, et al. Authentication of sea buckthorn oil based on non-targeted metabolomic[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(18): 246−253.
[25] 刘俊霞, 赵萍, 万小辉, 等. 大鲵肝茶叶水提液脱腥过程中挥发性有机物的动态变化[J]. 食品与机械,2022(3):38. [LIU J X, ZHAO P, WAN X H, et al. Dynamic changes of volatile organic compounds in giant salamander liver during the deodorization with tea water extract[J]. Food & Machinery,2022(3):38.] LIU J X, ZHAO P, WAN X H, et al. Dynamic changes of volatile organic compounds in giant salamander liver during the deodorization with tea water extract[J]. Food & Machinery, 2022(3): 38.
[26] 吴奇霄, 余松柏, 马龙, 等. 基于LC-MS和GC-MS结合多元统计的白酒酚类成分分析[J]. 中国酿造,2022,41(12):223−229. [[WU Q X, YU S B, MA L, et al. Component analysis of phenols in Baijiu based on LC-MS and GC-MS combined with multivariate statistics[J]. China Brewing,2022,41(12):223−229.] [WU Q X, YU S B, MA L, et al. Component analysis of phenols in Baijiu based on LC-MS and GC-MS combined with multivariate statistics[J]. China Brewing, 2022, 41(12): 223−229.
[27] 闫如毓, 郝慧宜, 苗子健, 等. 浓香型白酒发酵过程中4-甲/乙基愈创木酚的代谢规律分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2023,49(11):41−46. [YAN R Y, HAO H Y, MIAO Z J, et al. Analysis of metabolism of 4-methyl/ethyl guaiacol during strong flavor Baijiu fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023,49(11):41−46.] YAN R Y, HAO H Y, MIAO Z J, et al. Analysis of metabolism of 4-methyl/ethyl guaiacol during strong flavor Baijiu fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2023, 49(11): 41−46.
[28] XIONG Y X, ZHANG P Z, WARNER R D, et al. Sorghum grain:From genotype, nutrition, and phenolic profile to its health benefits and food applications[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2019,18(6):2025−2046. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12506
[29] 李行, 吴李玲, 裴荣红, 等. 6种武陵酱香型白酒中挥发性含硫化合物差异分析[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2024,42(1):83−93. [LI X, WU L L, PEI R H, et al. Distribution difference analysis of volatile sulfur-containing compounds in 6 kinds of Wuling soy sauce aroma-type Baijiu[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2024,42(1):83−93.] LI X, WU L L, PEI R H, et al. Distribution difference analysis of volatile sulfur-containing compounds in 6 kinds of Wuling soy sauce aroma-type Baijiu[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2024, 42(1): 83−93.
[30] 王韵, 汪峰, 费静娴, 等. 采供血机构ALT初筛检测质量保证的探讨[J]. 临床血液学杂志,2022,35(12):884−887. [WANG Y, WANG F, FEI J X, et al. Discussion on quality assurance of ALT primary screening in blood collection and supply institutions[J]. Journal of Clinical Hematology,2022,35(12):884−887.] WANG Y, WANG F, FEI J X, et al. Discussion on quality assurance of ALT primary screening in blood collection and supply institutions[J]. Journal of Clinical Hematology, 2022, 35(12): 884−887.
[31] ZHOU Y, LV J, YU Z, et al. Integrated metabolomics and transcriptomic analysis of the flavonoid regulatory networks in sorghum bicolor seeds[J]. BMC Genomics,2022,23(1):1−10. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08243-4
[32] CHMIEL M, STOMPOR-GORACY M. The spectrum of pharmacological actions of syringetin and its natural derivatives—a summary review[J]. Nutrients,2022,14(23):5157. doi: 10.3390/nu14235157
[33] EISEN B, UNGAR Y, SHIMONI E. Stability of isoflavones in soy milk stored at elevated and ambient temperatures[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2003,51:2212−2215. doi: 10.1021/jf025783h
[34] XIONG Y, ZHANG P Z, WARNER R D, et al. Comprehensive profiling of phenolic compounds by HPLC-DAD-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS to reveal their location and form of presence in different sorghum grain genotypes[J]. Food Research International,2020,137:109671. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109671
[35] PAVLI O I, VLACHOS C E, KALLONIATI C, et al. Metabolite profiling reveals the effect of drought on sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) metabolism[J]. Plant Omics,2013,6(6):371−376.
[36] PAIVA LIBOREIRO C, PINHEIRO EVANGELISTA W, VIEIRA QUEIROZ V A, et al. Bioactive amines in sorghum:Method optimisation and influence of line, tannin and hydric stress[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,173:224−230. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.10.039
[37] 王新磊, 吕新芳. 氮代谢参与植物逆境抵抗的作用机理研究进展[J]. 广西植物,2020,40(4):583−591. [WANG X L, LÜ X F. Research progress on mechanism of nitrogen metabolism involved in plan stress resistance[J]. Guihaia,2020,40(4):583−591.] WANG X L, LÜ X F. Research progress on mechanism of nitrogen metabolism involved in plan stress resistance[J]. Guihaia, 2020, 40(4): 583−591.
[38] CHEN L J, ZHAO X, PLUMMER S, et al. Quantitative determination and structural characterization of isoflavones in nutrition supplements by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatograohy,2005,1082:60−70. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2005.03.066
[39] LÓPEZ-GUTIÈRREZ N, ROMERO-GONZÁLEZ R, FRENICH A G, et al. Identification and quantification of the main isoflavones and other phytochemicals in soy based nutraceutical products by liquid chromatography-orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2014,1348:125−136. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.04.090
[40] XIE B G, LIU Y L, ZOU H Q, et al. Determination of D-glucaric acid and/or D-glucaro-1, 4-lacton in different apple varieties through hydrophilic interaction chromatography[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,203:1−7. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.02.009
[41] PEREZ J L, JAYAPRAKASHA G K, YOO K S, et al. Development of a method for the quantification of D-glucaric acid in different varieties of grapefruits by high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectra[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2008,1190:394−397. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2008.03.026
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 何欣芫,胡力,李春强,张燕维,孙卫青,邵俊花. 超声波及直流磁场对淘汰蛋鸡鸡胸肉糜理化性质和凝胶特性的影响. 现代食品科技. 2024(12): 178-187 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘树萍,冯爽,陆家慧,苏晓文,张佳美,石长波. 黑豆豆腐替代脂肪对肉丸品质特性的影响. 食品工业科技. 2022(08): 41-49 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 何惠利,任雪娇,张莉力. 蒲公英黄酮-壳聚糖复合膜的制备及对冷鲜鸡胸肉保鲜的研究. 食品研究与开发. 2022(07): 112-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王文艳,马长明,崔悦,杨雅新,魏贞,刘欣,王娟. 淘汰蛋鸡的肉质嫩化技术应用进展. 美食研究. 2022(03): 87-92 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 邹欣洋,计瑶,张晶,陈钰,孙晶. 复合香辛料提取物对冷藏猪肉糜氧化及品质特性的影响. 保鲜与加工. 2022(10): 23-31+39 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 周业飞,蔡垚,袁俊. 运动对淘汰蛋鸡肉用性能和肉品质的影响. 肉类研究. 2021(10): 13-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:



