Content and Antioxidant Activity of Active Components in Different Parts of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis
-
摘要: 为比较山栀子不同部位活性成分并评价各部位体外抗氧化活性,本文用超声辅助提取法提取山栀子不同部位有效成分,并测定得率;使用紫外-可见分光光度法测定总环烯醚萜、总藏红花素、总黄酮和总酚含量;利用高效液相色谱法测定山栀子不同部位活性成分单体;采用DPPH、ABTS+自由基清除试验评估其体外抗氧化能力,并进行活性成分与抗氧化活性的相关性分析。结果表明,山栀子叶中的总环烯醚萜和总酚含量最高,分别为244.87±5.89 mg·g−1和16.71±0.55 mg·g−1;山栀子果中的总藏红花素(16.18±1.40 mg·g−1)相较于其余部分存在显著性差异(P<0.05),其中藏红花素-Ⅰ为藏红花苷主要形式,约占总藏红花素的60%;山栀子花中的总黄酮含量最高43.61±1.01 mg·g−1。根据DPPH自由基、ABTS+自由基清除率试验,山栀子叶的抗氧化活性最好,IC50分别为36.00±2.70和31.96±3.87 μg·mL−1;经相关性分析发现环烯醚萜类化合物与酚类化合物与抗氧化能力呈强相关性。采用超声辅助提取法提取得到的山栀子不同部位活性成分,发现不同部位均具有一定抗氧化能力,同时叶具有超越果的抗氧化活性,为天然抗氧化剂的开发提供了理论来源。
-
关键词:
- 山栀子 /
- 不同部位 /
- 活性成分 /
- 高效液相色谱(HPLC) /
- 抗氧化活性
Abstract: To compare the active compounds in different parts of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis and evaluate their in vitro antioxidant activities, this study used the ultrasound-assisted method to extract the active compounds in different parts of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis and measured the yield. Their total iridoids, total crocins, total flavonoids and total polyphenols were measured by UV-visible spectrophotometer method. Their active compound monomers were measured by HPLC method. DPPH and ABTS+ radical scavenging methods were used to valuate their in vitro antioxidative activities then the correlation analysis was founded between the contents of active compounds and IC50 of DPPH and ABTS+ radical. Gardenia jasminoides Ellis leaf had the highest total iridoids contents and total polyphenols contents, which were 244.87±5.89 mg·g−1 and 16.71±0.55 mg·g−1 respectively. Results showed that, theGardenia jasminoides Ellis fruit had the significantly highest total crocins contents (P<0.05), which was 16.18±1.40 mg·g−1, Crocin-I was the main form of crocin, which occupied about 60% of the total crocin contents. Gardenia jasminoides Ellis flower had the highest total flavonoids contents and, which was 43.61±1.01 mg·g−1. According to DPPH and ABTS+ radical scavenging experiments, the Gardenia jasminoides Ellis leaf had the best antioxidative activities, which IC50 of DPPH and ABTS+ were 36.00±2.70 and 31.96±3.87 μg·mL−1. The correlation analysis showed that iridoids compounds and polyphenols compounds had strong correlation with antioxidative activities. Among the different parts of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis extracted by ultrasound-assisted method, it was found that different parts had certain antioxidant capacity. Gardenia jasminoides Ellis leaf had antioxidative activities beyond the fruit, which provided theoretical sources for development of natural antioxidants. -
栀子(Gardenia jasminoids Ellis)是茜草科栀子属植物,又称白蟾、山栀子、黄栀子,属于国家卫生部第一批药食同源物品。栀子果实中含有多种活性成分,如京尼平苷、藏红花素、绿原酸等[1],具有丰富的生物药理活性,如抗氧化、保肝利胆、抗炎、抗癌、降血糖血脂、抑菌等[2−6]。但是对栀子的研究主要集中在果实中,而对其余不同部位活性成分的研究较少,尤其是根、枝、叶。
关于栀子不同部位的相关研究如下,Chen等[7]采用超声辅助提取法提取栀子果中的活性成分,其中关键活性成分为京尼平龙胆苷、京尼平苷、藏红花素-1、藏红花素-2,并研究发现栀子果醇提物具有抗高血压作用,且可能与京尼平苷有关。Hu等[8]比较了栀子花与栀子果醇提物中的活性成分,发现栀子花中含有的羟异京尼平苷含量较京尼平苷更高,栀子果相反,表明栀子花与栀子果的活性用途存在一定差异。有关栀子根和枝的研究较少,仅可知根中含有环烯醚萜、皂苷等活性成分[9]。Khac等[10]对栀子叶的醇提取物进行化学分析,分离出新环烯醚萜成分,此外还发现其具有抗炎活性。目前对栀子的研究主要是对单一部位的研究,对栀子不同部位的成分和抗氧化活性间的差异性未进行集中对比分析。
环烯醚萜化合物、黄酮化合物、酚类化合物等作为天然抗氧化剂的主要功能成分,对DPPH等自由基具有优越的清除能力[11−13]。藏红花素作为一种天然抗氧化剂[14],仅存在于栀子和藏红花中,具有极高的药理活性。由于不同产地、不同品种的栀子表现出较大的成分和活性差异[15],故以山栀子为原料,采用超声辅助提取法制备不同部位醇提物,以环烯醚萜、藏红花素、黄酮、多酚含量为主要活性成分指标,以DPPH、ABTS+自由基清除率探究体外抗氧化活性,对比不同部位活性成分与抗氧化活性差异性,以期为山栀子全株的综合利用及天然抗氧化剂的发展提供多样的原料和理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
山栀子不同部位(叶、枝、根、花、果) 采自浙江农林大学平山基地;无水乙醇、甲醇、氢氧化钠、乙酸铵、冰乙酸、亚硝酸钠等 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)、2,2′-联氮-双(3-乙基苯并噻唑-6-磺酸)二铵盐(ABTS)、抗坏血酸(Vitamin C,Vc)、京尼平苷标准品等 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;乙腈、甲醇 色谱纯,美国Tedia公司;以上分离用试剂均为分析纯。
RV3 eco旋转蒸发仪 IKA公司;UV-5500紫外可见分光光度计 上海元析仪器有限公司;Essentia LC-16高效液相色谱仪 日本岛津公司;Freezone 18 L冷冻速干机 LABCONCO公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 乙醇提取物制备
参考刘芳等[16]的方法使用超声辅助提取栀子中活性成分,称取一定质量山栀子不同部位粉末,按1:30的料液比加入70%乙醇,在60 ℃,100 W条件下超声辅助提取1.5 h,2次。抽滤获得滤液后使用旋转蒸发仪40 ℃蒸发溶剂,获得浓缩液。将浓缩液−80 ℃预冻24 h后进行冷冻干燥,获得山栀子乙醇提取物,并计算得率,计算公式如下:
得率(%)=mn×100 (1) 式中,m为冻干粉质量(g);n为所称取不同部位粉末质量(g)。
1.2.2 总环烯醚萜含量测定
参考曲书阅等[17]的方法,以京尼平苷为标准品在238 nm波长下绘制标准曲线,得到标准曲线为Y=0.0106X+0.0253(R2=0.9915),样品所得结果以京尼平苷(mg/g)含量表示。
1.2.3 总藏红花素含量测定
参考陈雁等[18]的方法,以藏红花素-Ⅰ为标准品在440 nm波长绘制标准曲线,得到标准曲线为Y=0.0709X+0.0338(R2=0.9982),藏红花素-Ⅰ浓度于1~20 μg·mL−1范围内线性关系良好,样品所得结果以藏红花素-Ⅰ(mg/g)含量表示。
1.2.4 总黄酮含量测定
采用硝酸-亚硝酸钠比色法进行总黄酮含量的测定,参考倪勤学等[19]的方法,以芦丁为标准品在510 nm波长绘制标准曲线,得到标准曲线为Y=0.1275X+0.0427(R2=0.9992),芦丁浓度于7.5~60 μg·mL−1范围内线性关系良好,样品所得结果以芦丁(mg/g)含量表示。
1.2.5 总酚含量测定
参考郑茜等[20]的方法进行修改,采用福林酚比色法,以没食子酸为标准品在765 nm波长绘制标准曲线,得到标准曲线为Y=0.0061X+0.074(R2=0.9998),没食子酸浓度于1~100 μg·mL−1范围内线性关系良好,样品所得结果以没食子酸(mg/g)含量表示。
1.2.6 环烯醚萜类成分测定
参考勾晓丹[21]的方法进行调整获得HPLC色谱条件:Welth ODS-3色谱柱(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm),波长238 nm,进样量10 μL,柱温35 ℃,A相为0.1%磷酸水溶液、B相为乙腈,梯度洗脱程序为:0 min 10% B、0~5 min 10% B~50% B、5~8 min 50%~95% B、8~12 min 95% B、12~13 min 95%~10% B、13~20 min 10% B。以京尼平苷、京尼平、京尼平苷酸、羟异京尼平苷为标准品制作混标溶液,经0.45 μm滤膜后进HPLC分析制备标准曲线,得到的标准曲线分别为Y=20946X+5336(R2=0.9995)、Y=43413X−49177(R2=0.9983)、Y=9054X−3025(R2=0.9999)、Y=15932X−58631(R2=0.9995),并分别在1~100 μg·mL−1、1~100 μg·mL−1、1~100 μg·mL−1、2.4~600 μg·mL−1范围内线性关系良好,样品所得结果分别以京尼平苷(mg/g)、京尼平(mg/g)、京尼平苷酸(μg/g)、羟异京尼平苷(mg/g)含量表示。
1.2.7 藏红花苷类成分测定
通过参考GB 5009.149-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中栀子黄的测定》[22]获得HPLC色谱条件:Welth ODS-3色谱柱(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm),波长440 nm,进样量10 μL,柱温35 ℃,A相为乙酸-乙酸铵(pH=4)、B相为乙腈,梯度洗脱程序为:0~1 min 20% B、1~8 min 20%~60% B、8~8.1 min 60%~70% B、8.1~13 min 70%~98% B、13~15 min 98%~20% B、15~20 min 20% B。以藏红花素-Ⅰ、藏红花素-Ⅱ、藏红花酸为标准品制作混标溶液,经0.45 μm滤膜后进HPLC分析制备标准曲线,得到标准曲线分别为Y=55690X−44464(R2=0.9992)、Y=63920X−24781(R2=0.9979)、Y=371592X−110595(R2=0.9992),并均在1~40 μg·mL−1范围内线性关系良好,样品所得结果以藏红花素-Ⅰ(mg/g)、藏红花素-Ⅱ(mg/g)、藏红花酸(μg/g)含量表示。
1.2.8 DPPH自由基清除能力的测定
参考Li等[23]的方法进行调整,吸取0.1 mL不同浓度的山栀子叶(12.50~300 μg/mL)、枝(75~300 μg/mL)、根(75~300 μg/mL)、花(75~300 μg/mL)、果(25~300 μg/mL)提取物溶液和95%乙醇溶液(空白对照),加入3.9 mL的DPPH溶液,混合均匀,避光静置30 min,于517 nm波长下测定吸光度,计算DPPH自由基清除率,并计算清除率达到50%时所需要的样品质量浓度(IC50,μg·mL−1),计算公式如下。同时以抗坏血酸(Vitamin C,VC)为阳性对照。
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 (2) 式中,A0为DPPH溶液和乙醇的吸光度;A1为DPPH溶液和不同浓度山栀子不同部位乙醇提取液的吸光度;A2为乙醇和不同浓度山栀子不同部位乙醇提取液的吸光度。
1.2.9 ABTS+自由基清除能力测定
参照Thambiraj等[24]的方法进行调整,吸取0.1 mL不同浓度的提取物溶液(10~100 μg/mL)和95%乙醇溶液(空白对照),加入3.9 mL的ABTS+自由基工作液,混合均匀,室温下避光反应5 min,于734 nm处测定其吸光度。计算ABTS+自由基清除率,并计算IC50,计算公式如下。同时以抗坏血酸(Vitamin C,VC)为阳性对照。
ABTS+自由基清除率(%)=(1−An−AmAs)×100 (3) 式中,As为ABTS+自由基工作液和乙醇的吸光度;An为ABTS+自由基工作液和不同浓度山栀子不同部位乙醇提取液的吸光度;Am为乙醇和不同浓度山栀子不同部位乙醇提取液的吸光度。
1.3 数据处理
每个实验进行三次平行,结果以平均值±标准差表示;采用Excel 2016、IBM SPSS Statistics 21进行实验数据分析,方差分析使用Duncan检验;采用Origin 2021进行作图与相关性分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 活性成分含量
2.1.1 山栀子乙醇提取物得率
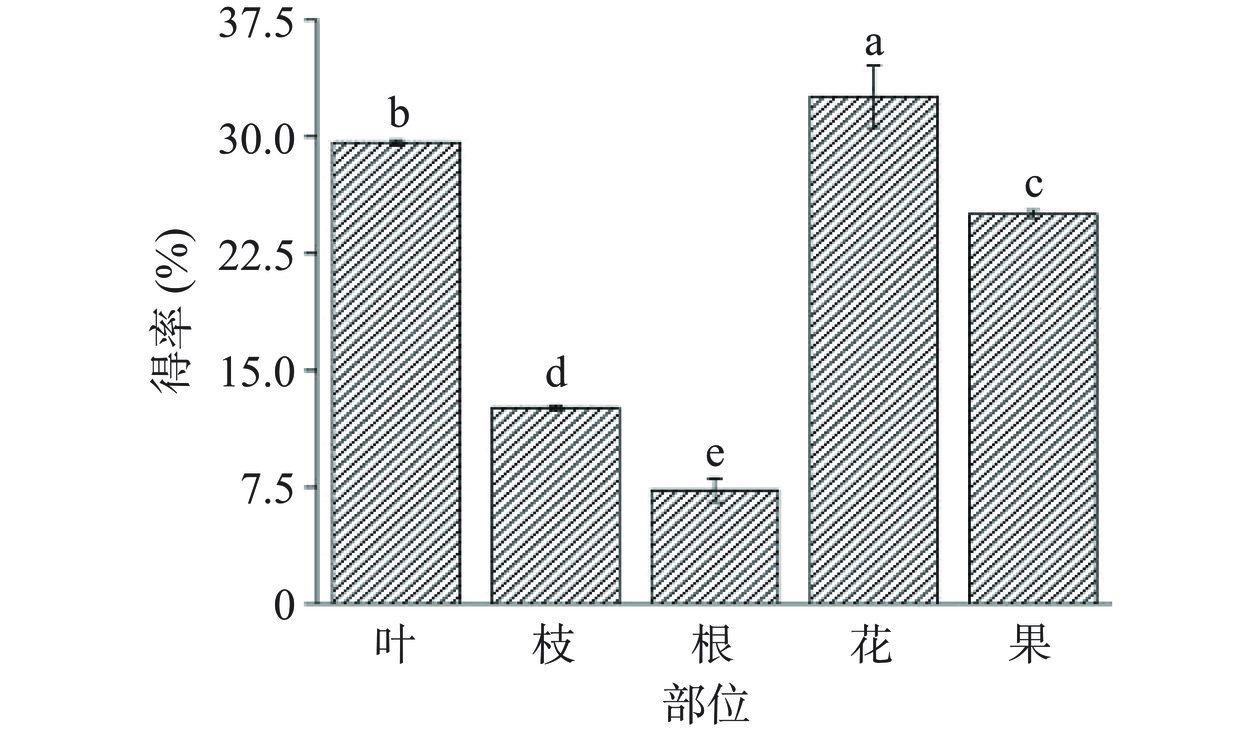
超声辅助提取法通过破坏植物细胞结构来进一步释放其中的活性成分,使其得率更高。如图1所示,以70%乙醇溶液为溶剂采用超声辅助提取在60 ℃,100 W的条件下对山栀子不同部位活性成分进行提取,得率在7.30%~32.58%之间。黄硕等[25]研究发现栀子叶70%乙醇提取物可能是通过抑制酪氨酸酶活性,来抑制α-MSH诱导发生的B16黑色素瘤细胞黑色素的生成。而栀子叶采用超声辅助提取时,得率接近30%,产率较高,因此对栀子叶中的活性成分进行研究,对开发天然食品抗氧化剂等产品有一定潜力。
2.1.2 总环烯醚萜含量
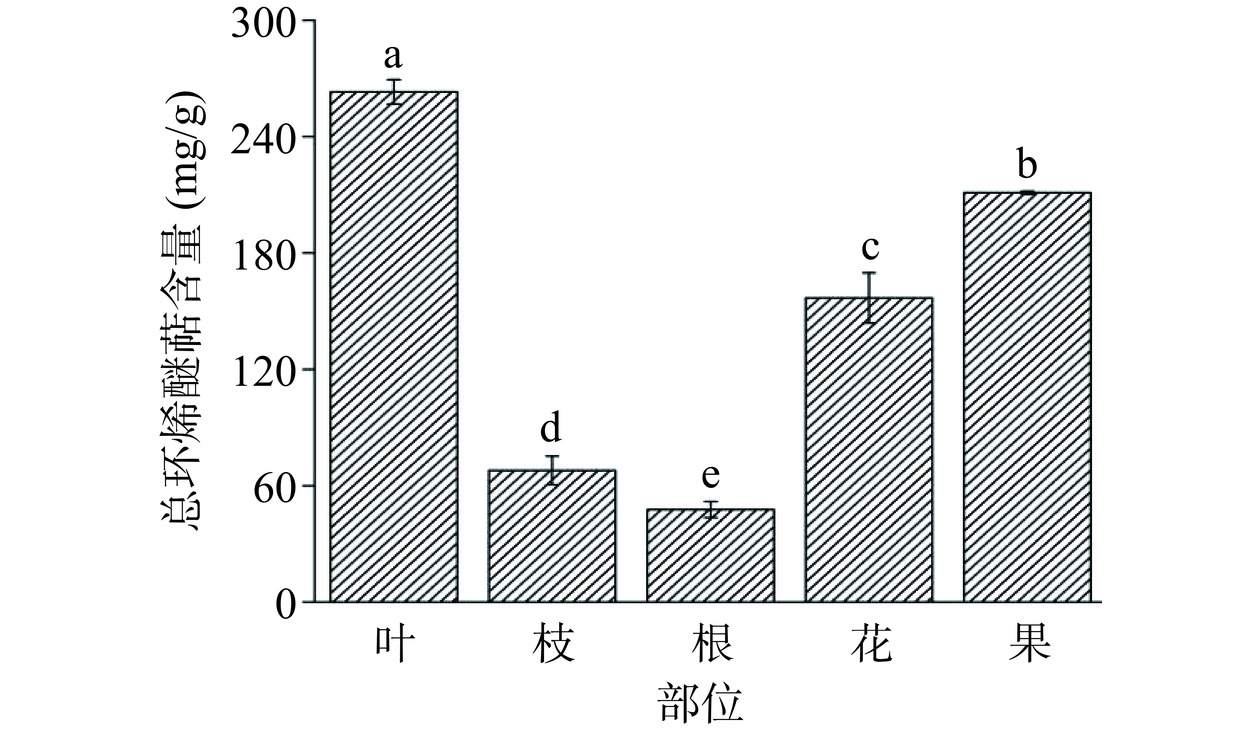
环烯醚萜类化合物在植物体内广泛存在,主要存在于双子叶植物中[26]。环烯醚萜类化合物是栀子中最主要活性成分之一,主要为京尼平苷。通过对山栀子不同部位的总环烯醚萜含量进行测定,如图2所示,不同部位中的总环烯醚萜含量存在显著性差异(P<0.05),而其中叶中所含总环烯醚萜含量最高,与果相近,约为枝的3.6倍,根的5倍之多。将山栀子五个部位按总环烯醚萜含量自高到低进行排列,依次为叶(244.87±5.89 mg·g−1)>果(211.15±0.75 mg·g−1)>花(156.83±12.97 mg·g−1)>枝(67.86±7.36 mg·g−1)>根(47.69±4.17 mg·g−1)。与山茱萸果实相比,栀子叶、花、果中的环烯醚萜类化合物的含量更高[27],因此叶、花、果可以作为环烯醚萜类化合物提取、分离的潜在植物来源。
2.1.3 总藏红花素含量
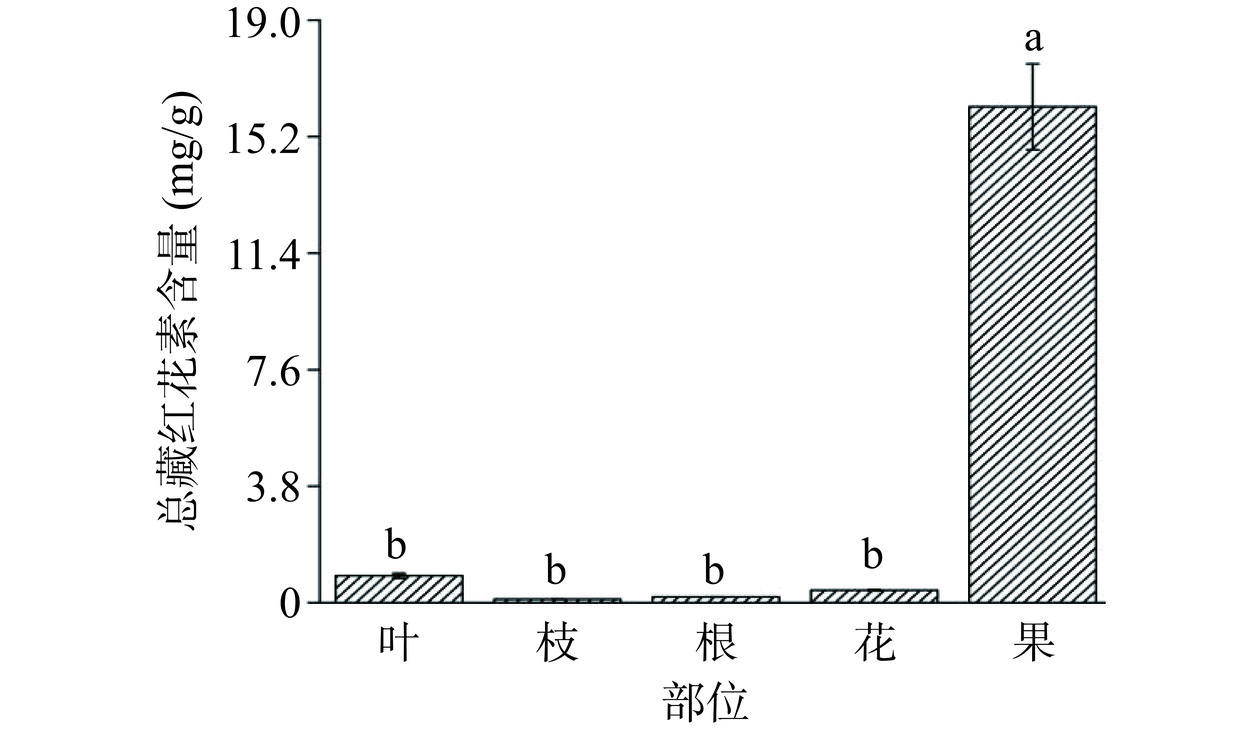
藏红花素的植物来源较少,主要在栀子和藏红花中被广泛检出。且藏红花素作为栀子中的主要活性成分,为栀子黄的主要显色成分。如图3所示,除栀子果外其余部位藏红花素几乎未检出,而栀子果中的总藏红花素含量为16.18±1.40 mg·g−1,相较于藏红花而言,栀子中的总藏红花素含量更低[28],但由于栀子的成本比藏红花低好几倍,因此现在对于藏红花素的提取多是以栀子作为原料。现如今,以玉米黄质为底物来进行藏红花素的生物合成[29],也将成为藏红花素的重要来源。
2.1.4 总黄酮含量
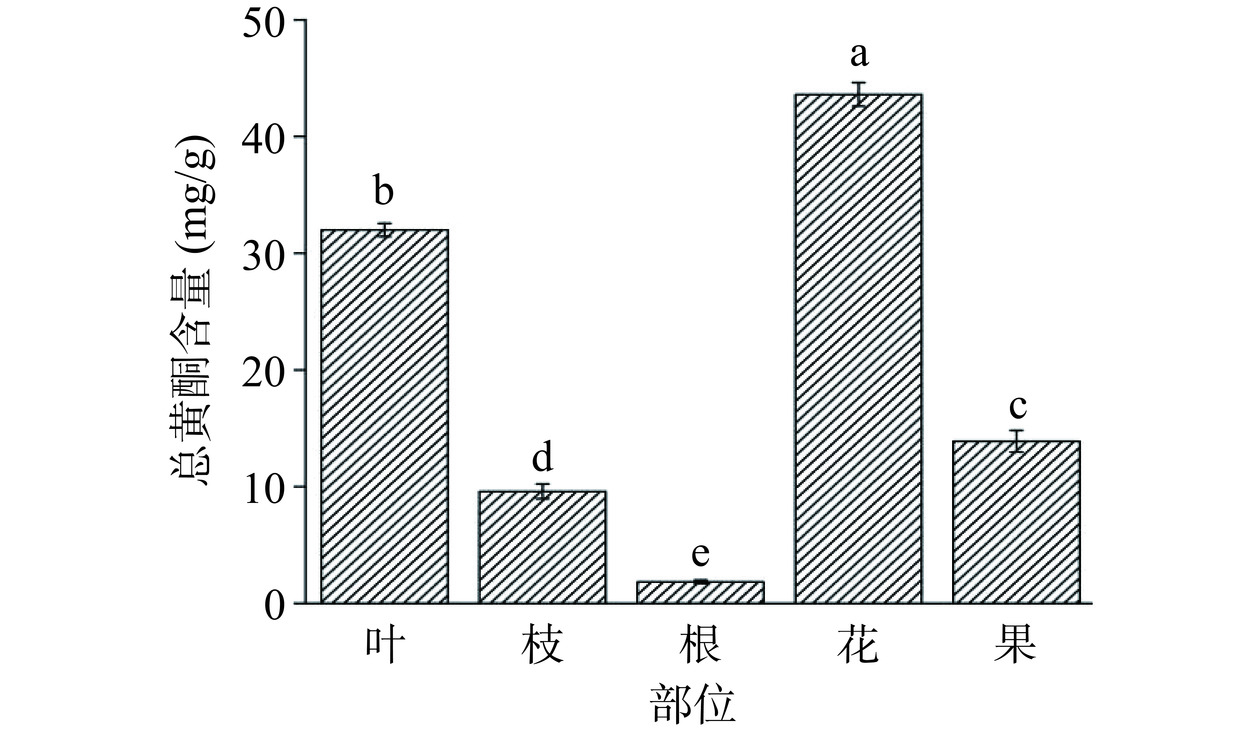
黄酮类化合物是植物光合作用产生的次生代谢产物,植物体各器官中的含量会因其酶的分布存在一定差异[30]。如图4所示,山栀子不同部位中总黄酮含量存在显著性差异(P<0.05),表现为花(43.61±1.01 mg/g)>叶(32.00±0.57 mg/g)>果(13.89±0.93 mg/g)>枝(9.59±0.63 mg/g)>根(1.84±0.15 mg/g),相较于黄潇等[31]对栀子花总黄酮含量测定值更高。同时Tajuddeen等[32]发现栀子叶甲醇提取物具有抗疟疾的功效,并且分离发现是叶中的黄酮和皂苷起到主要活性作用。
2.1.5 总酚含量
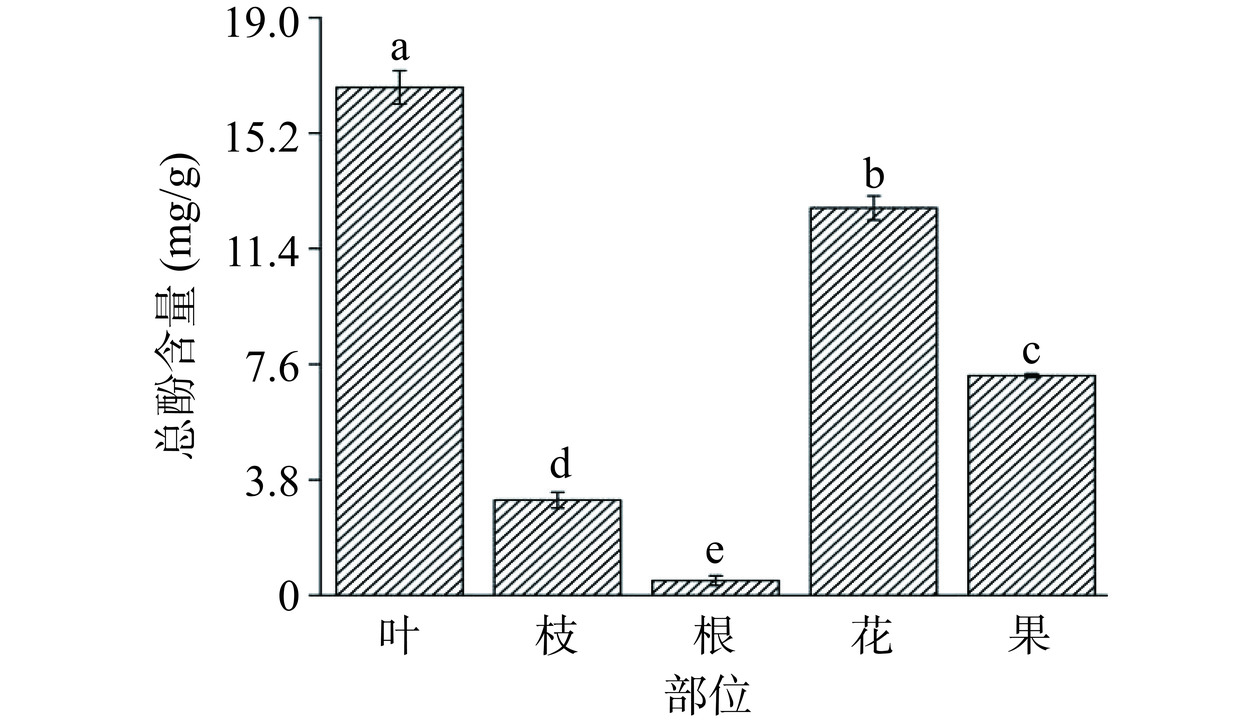
植物多酚是代谢过程中产生的重要次生代谢物之一[33],因其优越的抗氧化性,常被当作天然抗氧化剂使用,如茶多酚。如图5所示,山栀子不同部位中总酚含量存在显著性差异(P<0.05),表现为叶(16.71±0.55 mg/g)>花(12.74±0.40 mg/g)>果(7.23±0.06 mg/g)>枝(3.13±0.26 mg/g)>根(0.48±0.16 mg/g)。
2.1.6 环烯醚萜类成分含量
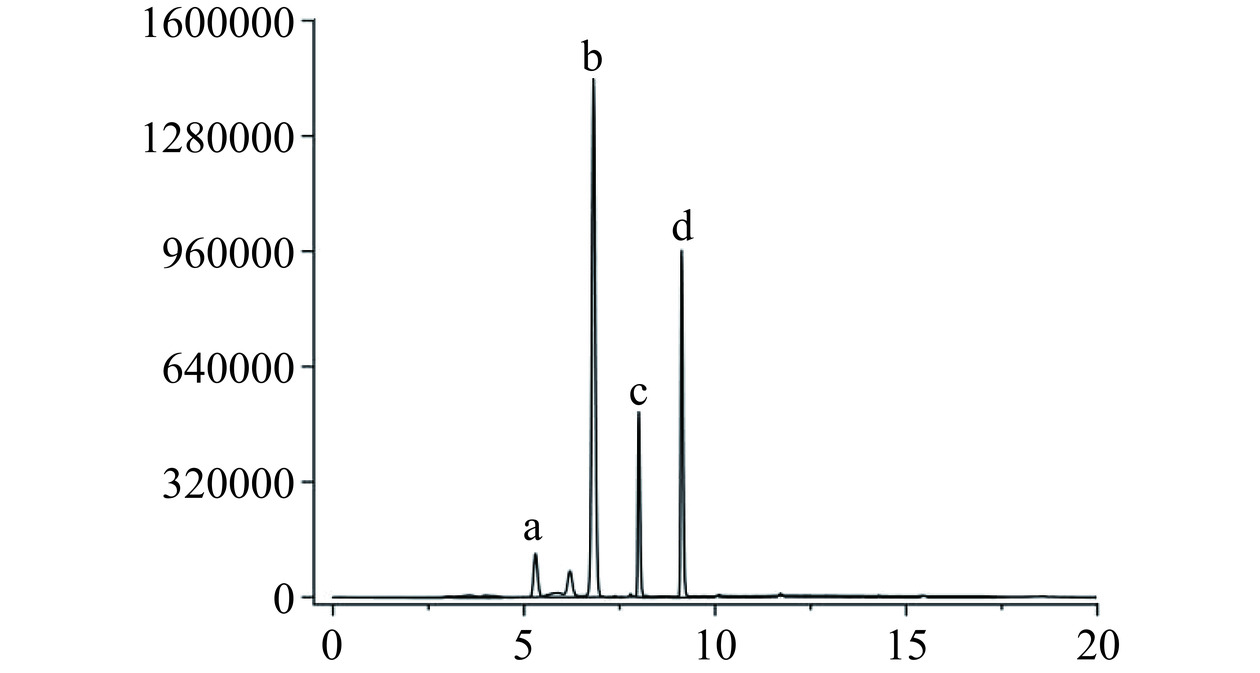
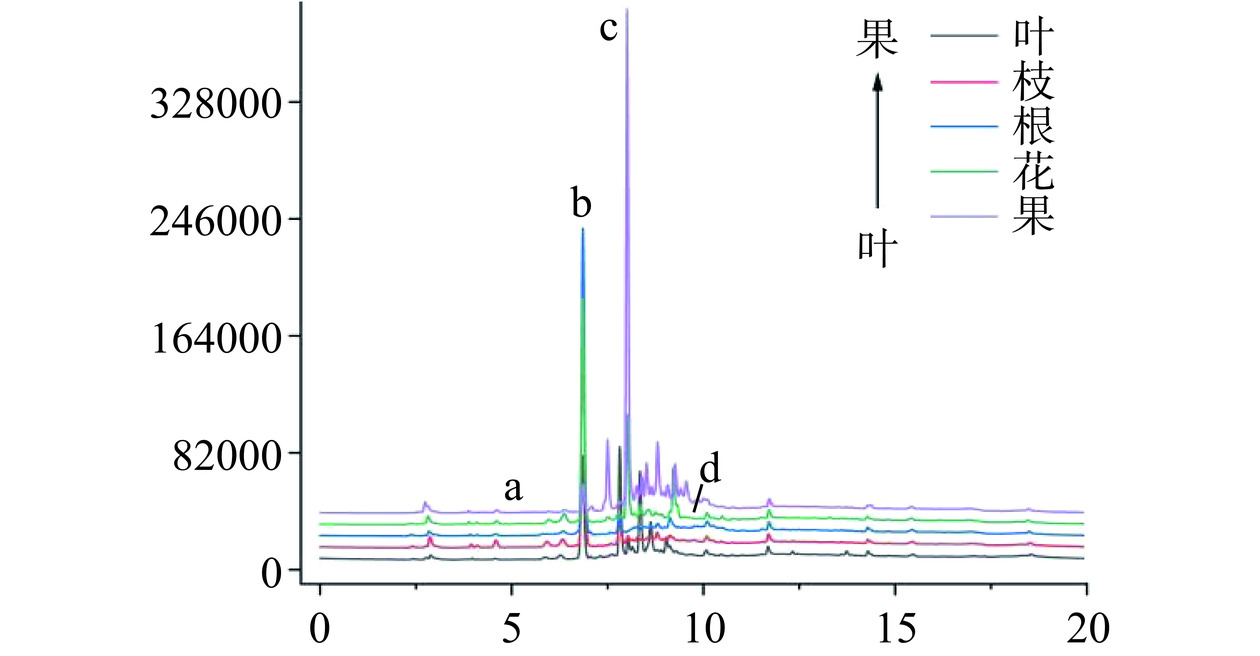
对比图6~图7和表1,山栀子不同部位中的主要环烯醚萜类化合物不同,果中主要是以京尼平苷的形式存在,含量为32.85±0.78 mg·g−1。而在叶、枝、根、花四个部位中,羟异京尼平苷则是主要成分,花中的羟异京尼平苷含量最高,为44.02±2.36 mg·g−1,相反果中的羟异京尼平苷含量最低,仅有5.02±0.62 mg·g−1。而京尼平和京尼平苷酸在五个部位中都几乎未检出,原因是京尼平上的C1上的羟基性质较为活泼,一般都会与糖苷结合,以京尼平苷的形式存在[34]。羟异京尼平苷作为栀子的生物活性标志物,具有降低肝脂肪堆积的作用[35],当前羟异京尼平苷的提取主要是以栀子果为原料[36],而实验表明栀子花和栀子叶中的羟异京尼平苷资源更为丰富,便于进一步利用推进功能性食品的开发。
表 1 山栀子不同部位中环烯醚萜类单体含量Table 1. Iridoids monomer contents of different parts of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis部位 京尼平苷含量
(mg·g−1)京尼平苷酸含量
(μg·g−1)羟异京尼平苷含量(mg·g−1) 京尼平含量
(mg·g−1)叶 1.97±0.05c ND 20.73±1.33b 1.64±0.07a 枝 0.52±0.07d ND 17.35±0.84c 0.95±0.07b 根 ND 84.61±5.07c 15.78±1.48c 0.70±0.04c 花 12.01±0.83b 496.18±23.59a 44.02±2.36a ND 果 32.85±0.78a 301.75±8.40b 5.02±0.62d ND 注:表中同列不同字母表示具有显著性差异(P<0.05);ND表示未检出。 2.1.7 藏红花苷类成分含量
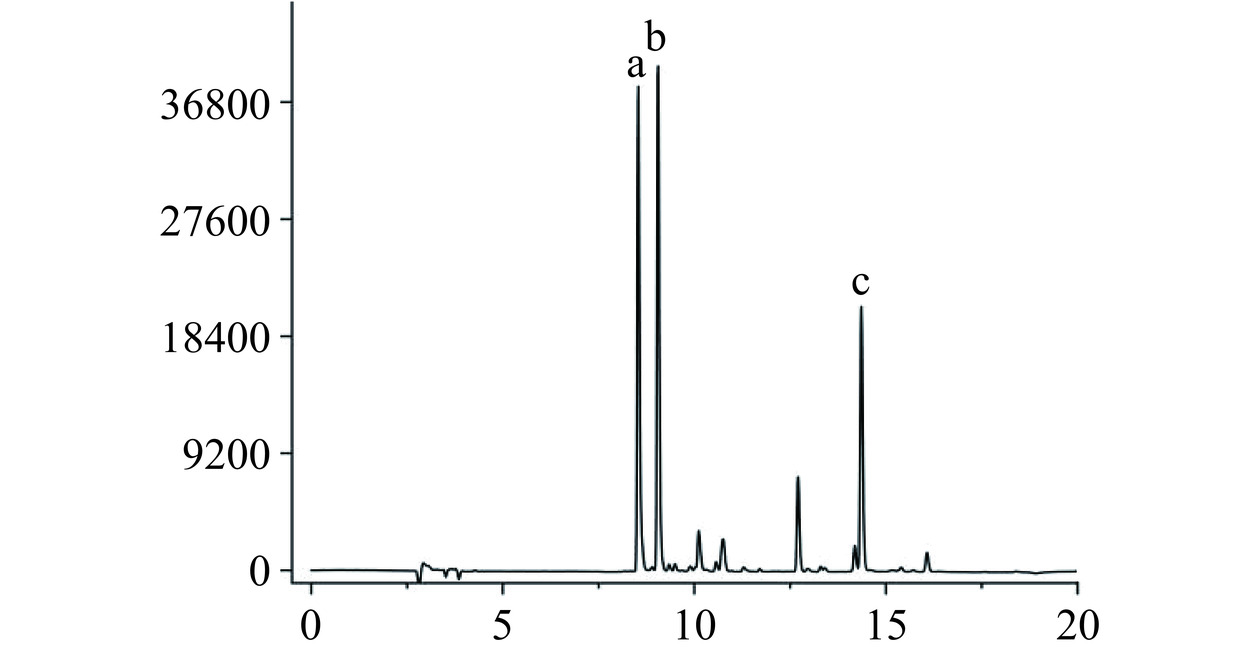
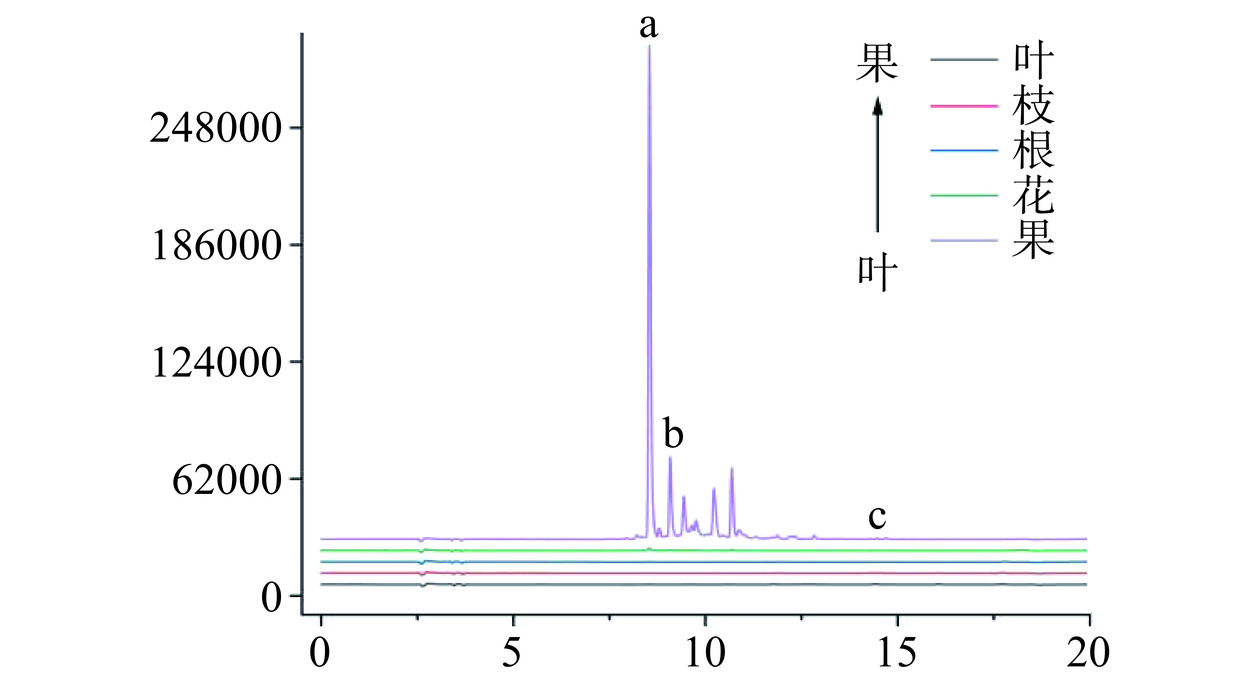
如图8~图9和表2所示,除山栀子果外,山栀子其余部位几乎未检测出藏红花苷类单体成分。果中含有藏红花素-Ⅰ、藏红花素-Ⅱ,含量为9.94±0.25和1.74±0.07 mg·g−1,结合上述对总藏红花素的测定,可以得出果中的藏红花素主要以藏红花素-Ⅰ的形式存在,占总藏红花素的61.43%与陈雁等[18]测定几乎一致。
表 2 山栀子不同部位中藏红花素和藏红花酸含量Table 2. Crocin and crocetin contents of different parts of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis部位 藏红花素-Ⅰ含量
(mg·g−1)藏红花素-Ⅱ含量
(mg·g−1)藏红花酸含量
(μg·g−1)叶 ND ND 199.21±8.54a 枝 ND ND ND 根 ND ND ND 花 0.57±0.04b 0.26±0.02b ND 果 9.94±0.25a 1.74±0.07a 137.71±0.36b 注:表中同列不同字母表示具有显著性差异(P<0.05);ND表示未检出。 2.2 体外抗氧化活性
2.2.1 DPPH自由基清除能力
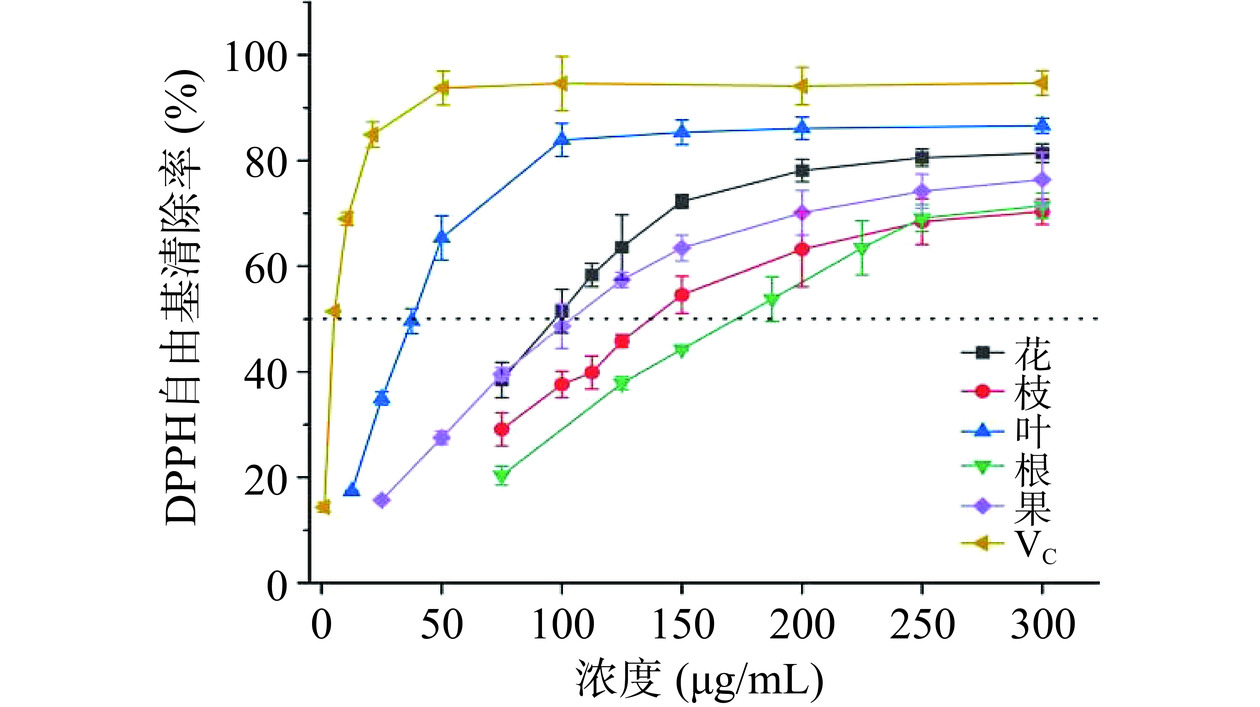
DPPH自由基清除能力模型被广泛用于评估样品体外抗氧化能力[37]。由图10可知,山栀子不同部位和VC对DPPH自由基的清除能力(以IC50为判断依据)为VC(5.13±0.70 μg/mL)>叶(36.00±2.70 μg/mL)>花(99.20±4.17 μg/mL)>果(124.98±14.99 μg/mL)>枝(134.85±12.81 μg/mL)>根(189.79±12.91 μg/mL),且DPPH自由基清除能力与样品浓度呈正相关。表明山栀子叶具有较好的抗氧化能力。
2.2.2 ABTS+自由基清除能力
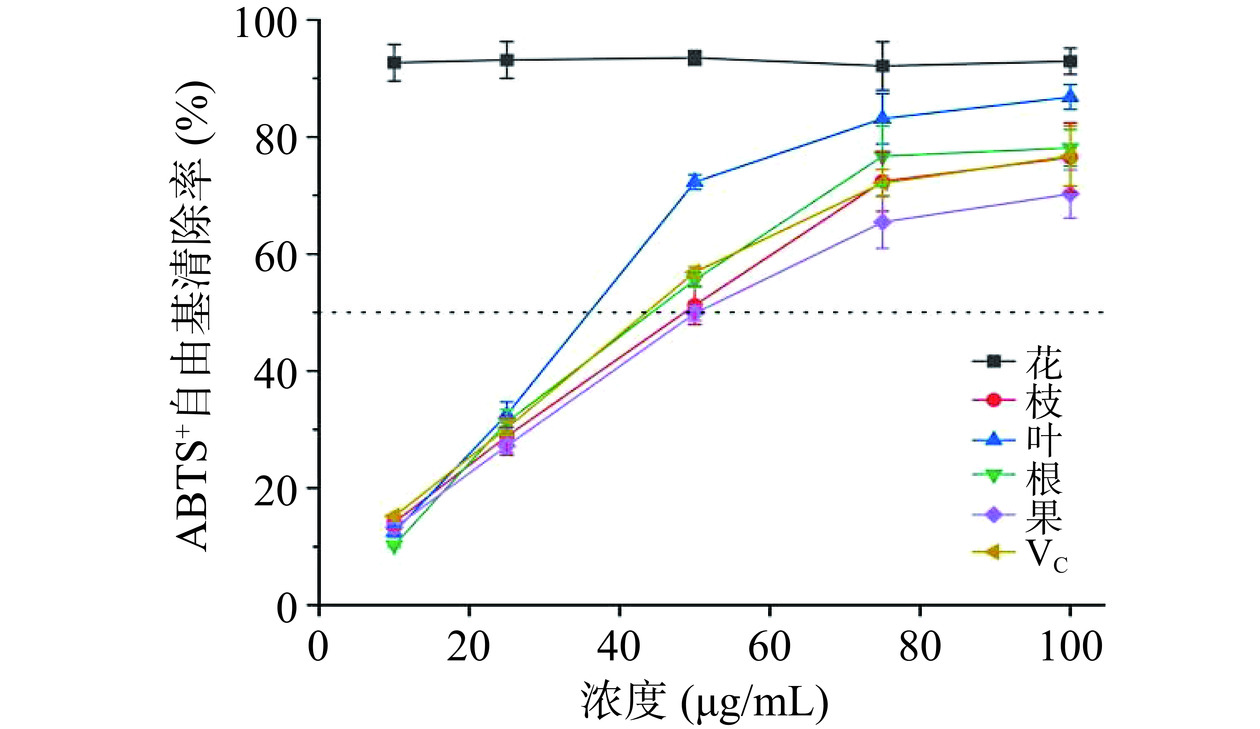
ABTS+自由基清除模型能够很好的判断供氢和断链抗氧化活性的有效方法[38]。如图11可知,山栀子不同部位和VC对ABTS+自由基清除能力为VC(2.01±0.01 μg/mL)>叶(31.96±3.87 μg/mL)>果(44.38±1.42 μg/mL)>根(44.98±0.51 μg/mL)>花(49.69±0.07 μg/mL)>枝(52.93±0.67 μg/mL),且ABTS+自由基清除能力与样品浓度呈正相关。
2.3 活性成分与抗氧化活性的相关性分析
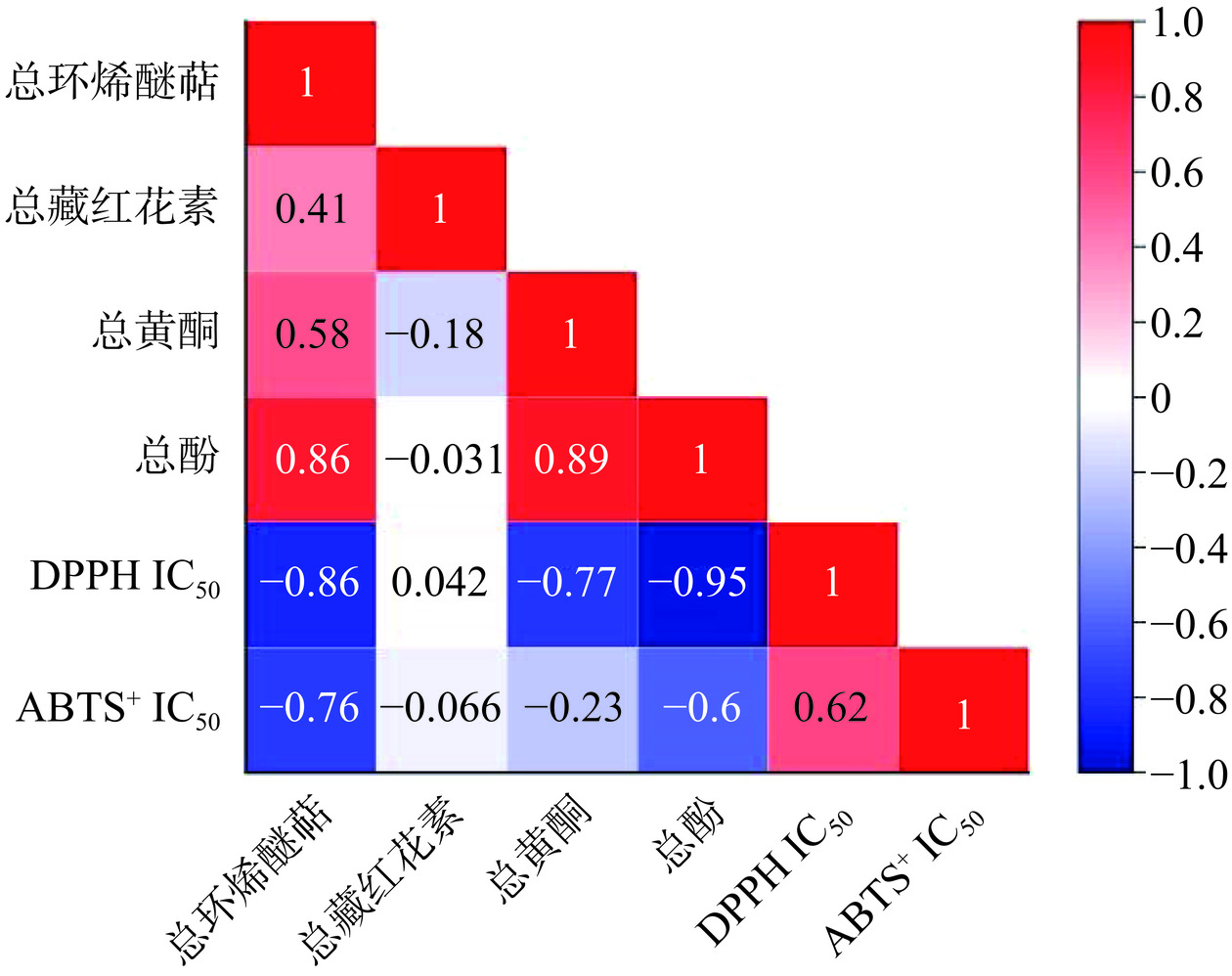
采用Pearson法对总环烯醚萜、总藏红花素、总黄酮、总酚与DPPH自由基清除能力、ABTS+自由基清除能力进行相关性分析,结果如图12所示。总环烯醚萜含量与DPPH自由基清除能力、ABTS+自由基清除能力呈强相关性,其相关系数分别为r=−0.86、r=−0.76,表明环烯醚萜类化合物具有一定的抗氧化能力。而总藏红花素含量与DPPH自由基清除能力、ABTS+自由基清除能力不呈相关性,表明藏红花苷类化合物与自由基结合能力较差。抗氧化活性与活性成分的相关性还取决于所运用的抗氧化模型相关[39],如总黄酮含量对DPPH自由基清除能力相关系数r=−0.77呈强相关,而对ABTS+自由基清除能力相关系数r=−0.23呈若相关,即可证明这一点。多酚因其丰富的酚羟基结构,可以提供活性氢直接与活性氧自由基相结合从而起到抗氧化作用[40],酚类物质一般具有极强的抗氧化能力,总酚含量与DPPH自由基清除能力、ABTS+自由基清除能力呈强相关性,且相关系数分别为r=−0.95、r=−0.6。
3. 结论
采用超声辅助提取法提取山栀子不同部位活性成分,提取率在7.30%~32.58%之间。测定总环烯醚萜、总藏红花素、总黄酮、总酚含量,其中叶中的总环烯醚萜含量与总酚含量最高,含量分别为244.87、16.71 mg·g−1;藏红花素作为栀子果的生物活性标志物,其余部位几乎未检出,果中总藏红花素含量为16.18 mg·g−1;花中的黄酮类化合物成分最多,总黄酮含量为43.61 mg·g−1。经HPLC鉴定得出叶、枝、根、花中的环烯醚萜主要为羟异京尼平苷,而果中的环烯醚萜主要为京尼平苷,同时果中的藏红花苷类成分主要为藏红花素-Ⅰ,占总藏红花素的61.43%。通过对DPPH自由基清除率、ABTS+自由基清除率的测试,发现叶的抗氧化能力最强,并且随着浓度的提高,其抗氧化能力也逐渐加强,IC50能分别达到36.0和31.96 μg·g−1,抗氧化能力较强,同时通过相关性分析,发现环烯醚萜化合物、黄酮化合物、酚类化合物与DPPH自由基清除率、ABTS+自由基清除率具有强相关性,而藏红花素苷类成分与二者具有弱相关,表明了叶的抗氧化能力优于果。本研究比较栀子不同部位活性成分与抗氧化活性,发现栀子叶、花、果三者均具有一定的抗氧化能力。上述结果可以为栀子不同部位的活性成分研究提供参考,同时栀子叶作为栀子加工利用过程中的废弃物,也提供了以栀子叶作为原料在天然抗氧化剂的开发利用方面提供一定理论依据。
-
表 1 山栀子不同部位中环烯醚萜类单体含量
Table 1 Iridoids monomer contents of different parts of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis
部位 京尼平苷含量
(mg·g−1)京尼平苷酸含量
(μg·g−1)羟异京尼平苷含量(mg·g−1) 京尼平含量
(mg·g−1)叶 1.97±0.05c ND 20.73±1.33b 1.64±0.07a 枝 0.52±0.07d ND 17.35±0.84c 0.95±0.07b 根 ND 84.61±5.07c 15.78±1.48c 0.70±0.04c 花 12.01±0.83b 496.18±23.59a 44.02±2.36a ND 果 32.85±0.78a 301.75±8.40b 5.02±0.62d ND 注:表中同列不同字母表示具有显著性差异(P<0.05);ND表示未检出。 表 2 山栀子不同部位中藏红花素和藏红花酸含量
Table 2 Crocin and crocetin contents of different parts of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis
部位 藏红花素-Ⅰ含量
(mg·g−1)藏红花素-Ⅱ含量
(mg·g−1)藏红花酸含量
(μg·g−1)叶 ND ND 199.21±8.54a 枝 ND ND ND 根 ND ND ND 花 0.57±0.04b 0.26±0.02b ND 果 9.94±0.25a 1.74±0.07a 137.71±0.36b 注:表中同列不同字母表示具有显著性差异(P<0.05);ND表示未检出。 -
[1] CHEN L P, LI M, YANG Z Q, et al. Gardenia jasminoides Ellis:Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacological and industrial applications of an important traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2020,257:112829. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112829
[2] 徐祯, 毛春芹, 顾薇, 等. 栀子花提取物的制备工艺优化及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2021,33(10):1720−1727,1796. [XU Z, MAO C Q, GU W, et al. Study on the optimization of the preparation technology of Gardenia jasminoides flower extract and its antioxidant activity[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2021,33(10):1720−1727,1796.] XU Z, MAO C Q, GU W, et al. Study on the optimization of the preparation technology of Gardenia jasminoides flower extract and its antioxidant activity[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2021, 33(10): 1720−1727,1796.
[3] CHEN P, CHEN Y, WANG Y, et al. Comparative evaluation of hepatoprotective activities of geniposide, crocins and crocetin by CCl4-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Biomolecules & Therapeutics,2016,24(2):156.
[4] OLIVEIRA H, CAI X, ZHANG Q, et al. Gastrointestinal absorption, antiproliferative and anti-inflammatory effect of the major carotenoids of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis on cancer cells[J]. Food & Function,2017,8(4):1672−1679.
[5] MENG X, WU C, LIU H, et al. Dietary fibers fractionated from gardenia (Gardenia jasminoides Ellis) husk:Structure and in vitro hypoglycemic effect[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2021,101(9):3723−3731. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.11003
[6] NYEMB J N, TCHUENGUEM R T, VENDITTI A, et al. Antimicrobial and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of chemical constituents from Gardenia aqualla (Rubiaceae)[J]. Natural Product Research,2022,36(24):6369−6374. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2022.2031187
[7] CHEN S, SUN P, ZHAO X, et al. Gardenia jasminoides has therapeutic effects on L-NNA-induced hypertension in vivo[J]. Molecular Medicine Reports,2017,15(6):4360−4373. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6542
[8] ZHANG H, FENG N, XU Y T, et al. Chemical constituents from the flowers of wild Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis[J]. Chemistry & Biodiversity,2017,14(5):e1600437.
[9] WANG J, LU J, LV C, et al. Three new triterpenoid saponins from root of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis[J]. Fitoterapia,2012,83(8):1396−1401. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2012.07.004
[10] KHAC H N, QUANG D N, QUANG L D, et al. New cycloartane coronalyl acetate and other terpenoids with anti-inflammatory activity from the leaves of Vietnamese Gardenia philastrei[J]. Natural Product Research,2023,37(19):3363−3367. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2022.2074004
[11] ZHANG F, YAN Y, ZHANG J, et al. Phytochemistry, synthesis, analytical methods, pharmacological activity, and pharmacokinetics of loganin:A comprehensive review[J]. Phytotherapy Research,2022,36(6):2272−2299. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7347
[12] WANG Y, LIU X J, CHEN J B, et al. Citrus flavonoids and their antioxidant evaluation[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2022,62(14):3833−3854. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1870035
[13] LIU H, JIANG W, CAO J, et al. Changes in extractable and non-extractable polyphenols and their antioxidant properties during fruit on-tree ripening in five peach cultivars[J]. Horticultural Plant Journal,2019,5(4):137−144. doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2019.04.005
[14] ALAVIZADEH S H, HOSSEINZADEH H. Bioactivity assessment and toxicity of crocin:A comprehensive review[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2014,64:65−80. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.11.016
[15] 陈家栋, 姜武, 黄宗贵, 等. 基于多指标分析的不同产地栀子质量研究[J]. 浙江农业科学,2023,64(2):323−327. [CHEN J D, JIANG W, HUANG Z G, et al. Study on the quality of Gardenia jasminoides from different origins based on multi-index analysis[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences,2023,64(2):323−327.] CHEN J D, JIANG W, HUANG Z G, et al. Study on the quality of Gardenia jasminoides from different origins based on multi-index analysis[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 64(2): 323−327.
[16] 刘芳, 颜彬, 龙吉财, 等. 栀子不同部位提取工艺优化与7种成分含量测定[J]. 湖南生态科学学报,2022,9(2):10−18. [LIU F, YAN B, LONG J C, et al. Optimization of extraction technology of different parts of Gardenia jasminoides and determination of seven components[J]. Journal of Hunan Ecological Science,2022,9(2):10−18.] LIU F, YAN B, LONG J C, et al. Optimization of extraction technology of different parts of Gardenia jasminoides and determination of seven components[J]. Journal of Hunan Ecological Science, 2022, 9(2): 10−18.
[17] 曲书阅, 衡霞, 戚懿予, 等. 栀子总环烯醚萜对抑郁模型小鼠神经递质的影响[J]. 中成药,2021,43(4):1022−1027. [QU S Y, HENG X, QI Y Y, et al. Effects of total iridoids of gardenia on neurotransmitters in depression model mice[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2021,43(4):1022−1027.] QU S Y, HENG X, QI Y Y, et al. Effects of total iridoids of gardenia on neurotransmitters in depression model mice[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2021, 43(4): 1022−1027.
[18] 陈雁, 张现涛. 栀子中藏红花总苷的提取纯化工艺研究[J]. 内蒙古中医药,2013,32(20):44−45. [CHEN Y, ZHANG X T. Study on extraction and purification technology of crocin in Gardenia jasminoides Ellis[J]. Inner Mongolia Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2013,32(20):44−45.] CHEN Y, ZHANG X T. Study on extraction and purification technology of crocin in Gardenia jasminoides Ellis[J]. Inner Mongolia Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 32(20): 44−45.
[19] 倪勤学, 高前欣, 徐志丰, 等. 2种栀子果主要经济性状及栀子果仁油成分分析[J]. 中国粮油学报,2017,32(10):78−84. [NI Q X, GAO Q X, XU Z F, et al. Analysis of main economic characters of two kinds of Gardenia jasminoides and components of their nut oil[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2017,32(10):78−84.] NI Q X, GAO Q X, XU Z F, et al. Analysis of main economic characters of two kinds of Gardenia jasminoides and components of their nut oil[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2017, 32(10): 78−84.
[20] 郑茜, 杨俊, 张富贵, 等. 凌霄花多酚微波提取工艺优化及其抗氧化研究[J]. 化学试剂,2021,43(9):1275−1280. [ZHENG Q, YANG J, ZHANG F G, et al. Study on microwave extraction process of polyphenols from Campsis radicans (L.) and its antioxidant activity[J]. Chemical Reagents,2021,43(9):1275−1280.] ZHENG Q, YANG J, ZHANG F G, et al. Study on microwave extraction process of polyphenols from Campsis radicans (L.) and its antioxidant activity[J]. Chemical Reagents, 2021, 43(9): 1275−1280.
[21] 勾晓丹. 高效液相色谱法测定栀子中藏红花素的含量[J]. 临床医药文献电子杂志,2019,6(39):179. [GOU X D. Determination of crocin content in gardenia by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Electronic Journal of Clinical Medical Literature,2019,6(39):179.] GOU X D. Determination of crocin content in gardenia by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Electronic Journal of Clinical Medical Literature, 2019, 6(39): 179.
[22] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.149-2016食品安全国家标准食品中栀子黄的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning Commision of the People’s Repubilc of China, National Medical Products Administration. GB5009.149-2016 National food safety standard Determination of gardenia yellow in food[S]. BeiJing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] National Health and Family Planning Commision of the People’s Repubilc of China, National Medical Products Administration. GB5009.149-2016 National food safety standard Determination of gardenia yellow in food[S]. BeiJing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[23] LI X C, LIN J, GAO Y X, et al. Antioxidant activity and mechanism of Rhizoma cimicifugae[J]. Chemistry Central Journal,2012,6(1):140. doi: 10.1186/1752-153X-6-140
[24] THAMBIRAJ S R, PHILLIPS M, KOYYALAMUDI S R, et al. Yellow lupin (Lupinus luteus L.) polysaccharides:Antioxidant, immunomodulatory and prebiotic activities and their structural characterisation[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,267:319−328. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.02.111
[25] 黄硕, 刘风. 栀子叶乙醇提取物对B16黑色素瘤细胞黑色素生成及酪氨酸酶活性的影响[J]. 中国当代医药,2020,27(36):4−7,12. [HUANG S, LIU F. Effect of ethanol extract of Fructus gardeniae leaves on the melanin formation and tyrosinase activity od B16 melanoma cells[J]. China Modern Medicine,2020,27(36):4−7,12.] HUANG S, LIU F. Effect of ethanol extract of Fructus gardeniae leaves on the melanin formation and tyrosinase activity od B16 melanoma cells[J]. China Modern Medicine, 2020, 27(36): 4−7,12.
[26] SU G Z, CAO Y, LI C, et al. Phytochemical and pharmacological progress on the genus Syringa[J]. Chemistry Central Journal,2015,9(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13065-015-0079-2
[27] KLYMENKO S, KUCHARSKA A Z, SOKÓŁ-ŁĘTOWSKA A, et al. Iridoids, flavonoids, and antioxidant capacity of Cornusmas, C. officinalis, and C. mas×C. officinalis fruits[J]. Biomolecules,2021,11(6):776. doi: 10.3390/biom11060776
[28] 王萌萌, 徐步斌, 周斌, 等. HPLC法测定西红花不同部位中西红花苷-Ⅰ和苷-Ⅱ[J]. 中成药,2019,41(5):1102−1105. [WANG M M, XU B B, ZHOU B, et al. Determination of crocin-Ⅰ and crocin-Ⅱ in different parts of Crocus sativus by HPLC[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2019,41(5):1102−1105.] WANG M M, XU B B, ZHOU B, et al. Determination of crocin-Ⅰ and crocin-Ⅱ in different parts of Crocus sativus by HPLC[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2019, 41(5): 1102−1105.
[29] SHEN T, ZHENG Y, LIU Q, et al. Integrated SMRT and illumina sequencing provide new insights into crocin biosynthesis of Gardenia jasminoides[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2022,23(11):6321. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116321
[30] 田云芳, 曹婷婷, 周明媚, 等. 黄瓜假还阳参不同部位黄酮提取及抗氧化活性[J]. 北方园艺, 2022(17):100-104. [TIAN Y F, CAO T T, ZHOU M M, et al. Extraction and antioxidant activity of flavonoids from different tissues of Crepidiastrum denticulatum[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2022(17):100-104.] TIAN Y F, CAO T T, ZHOU M M, et al. Extraction and antioxidant activity of flavonoids from different tissues of Crepidiastrum denticulatum[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2022(17): 100-104.
[31] 黄潇, 刘婧, 彭水梅, 等. 响应面法优化栀子中总多酚、总黄酮的提取工艺[J]. 中国药房,2017,28(28):3964−3968. [HUANG X, LIU J, PENG S M, et al. Optimization of extraction technology of total polyphenols and total flavonoids in Gardenia jasminoides by response surface method[J]. China Pharmacy,2017,28(28):3964−3968.] HUANG X, LIU J, PENG S M, et al. Optimization of extraction technology of total polyphenols and total flavonoids in Gardenia jasminoides by response surface method[J]. China Pharmacy, 2017, 28(28): 3964−3968.
[32] TAJUDDEEN N, SWART T, HOPPE H C, et al. Phytochemical and antiplasmodial investigation of Gardenia thunbergia L. f. leaves[J]. Natural Product Research,2022,36(16):4052−4060. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2021.1958808
[33] FARJADMAND F, KARIMPOUR-RAZKENARI E, NABAVI S M, et al. Plant polyphenols:Natural and potent UV-protective agents for the prevention and treatment of skin disorders[J]. Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry,2021,21(5):576−585. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666201109121246
[34] SHEN N, REN J, LIU Y, et al. Natural edible pigments:A comprehensive review of resource, chemical classification, biosynthesis pathway, separated methods and application[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,403:134422. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134422
[35] LIANG H, ZHANG L, WANG H, et al. Inhibitory effect of gardenoside on free fatty acid-induced steatosis in HepG2 hepatocytes[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2015,16(11):27749−27756. doi: 10.3390/ijms161126058
[36] CHEN L, WANG R, CUI L, et al. Preparation of five high-purity iridoid glycosides from Gardenia jasminoides Eills by molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction integrated with preparative liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Separation Science,2018,41(13):2759−2766. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201800086
[37] MUNTEANU I G, APETREI C. Analytical methods used in determining antioxidant activity:A review[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2021,22(7):3380. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073380
[38] ASADUZZAMAN A K M, HASAN I, RAHMAN M H, et al. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activity of phytoconstituents identified from Sargassum binderi seaweed extracts cultivated in Bangladesh[J]. Int. J. Biosci,2020,16(3):481−494.
[39] KUCHARSKA A Z, SOKÓŁ-ŁĘTOWSKA A, OSZMIAŃSKI J, et al. Iridoids, phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of edible honeysuckle berries (Lonicera caerulea var. kamtschatica Sevast.)[J]. Molecules,2017,22(3):405. doi: 10.3390/molecules22030405
[40] CAZZOLA M, CORAZZARI I, PRENESTI E, et al. Bioactive glass coupling with natural polyphenols:Surface modification, bioactivity and anti-oxidant ability[J]. Applied Surface Science,2016,367:237−248. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.01.138
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 欧阳丹,张超,杨莹,林振,苏来金. 6种组合酶法制备羊栖菜多糖的理化性质及其抗氧化活性. 食品工业科技. 2024(23): 248-257 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 范秋丽,张典铨,潘晨璐,林厦菁,苟钟勇,林志恒,叶金玲,丁发源,程忠刚,蒋守群. 饲粮添加栀子对黄羽肉鸡生长性能、血浆生化指标、免疫功能和抗氧化能力的影响. 动物营养学报. 2024(11): 6977-6988 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 贾延莎,张雪佳,谭宁华. 中药材中化学成分时空特异性的研究进展. 中草药. 2024(24): 8580-8588 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



